Patient monitors: how should they be used?
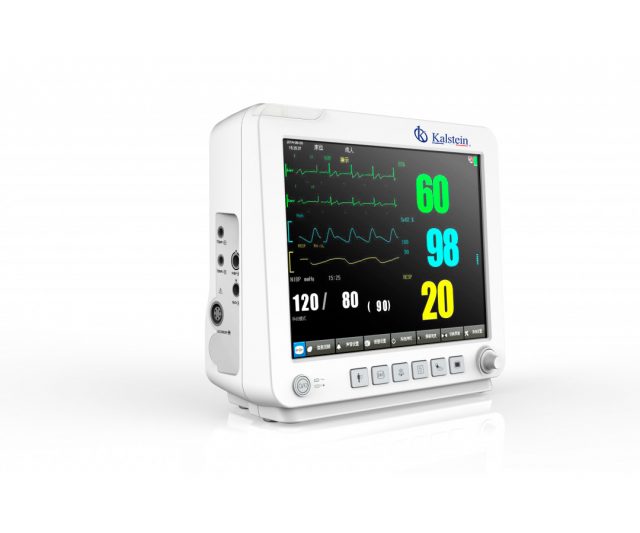
These workstations are part of the essential medical equipment in clinical centers, a patient monitor is a device that, combined with a system that is made up of different parameters, allows constant monitoring and storage of the patient’s vital signs; for this reason it is important that its use is as easy and simple to read.
What are the benefits of using an infusion pump?
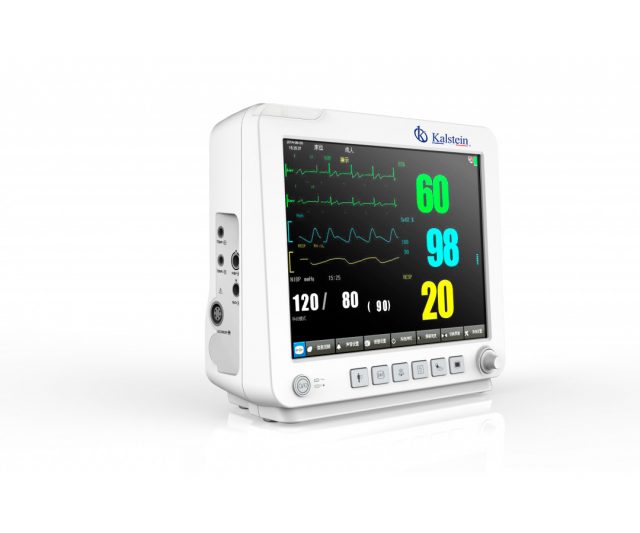
A patient monitor is a medical device that allows monitoring the vital signs of patients in critical condition and should be subjected to constant surveillance by medical personnel, in case of any alteration in the values of these; vital signs that are recorded with this equipment are: heart rate (ECG), respiratory rate (RESP), non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP), pulse (PR), oxygen saturation (SpO2), temperature (TEM), CO2 and invasive blood pressure (PAI).
Dissolved oxygen meter: How should it be used?

Oxygen meters are devices that use the amount of oxygen that is dissolved in or transported by a fluid, that is, a multi-capacity instrument for water quality inspection. Typically these equipment use two measuring scales: parts per million (ppm) or saturation percentage (%). Dissolved oxygen meters are used in the field and in laboratories.
What tests are performed in a pathology laboratory?

This area of medicine studies the morphological basis of the disease, that is, it is based on direct observation of the organ suffering from a disease, laboratories that are dedicated to this area carry out certain research methods such as microscopic observation based on histological, histochemical, electron microscope, immunohistochemical techniques, and more recently, of molecular techniques of special application in the pathology of cancer.
Water purification system: What systems exist in a laboratory?
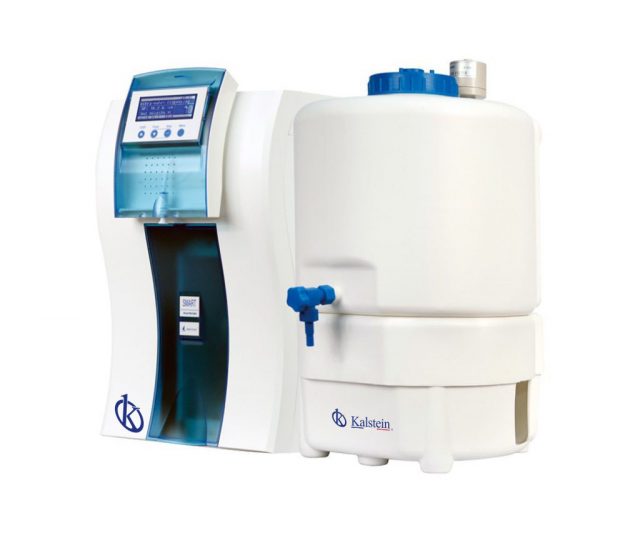

Good quality water is considered a key element to successfully carry out the analyzes and experiments that are carried out in laboratories. Laboratory water purification systems provide a source of pure water, continuously and alternatively, to carry out the different analyses, tests and experiments that are carried out in a laboratory.
Laboratory rotary evaporator: what is its importance in the chemical industry?

A rotary evaporator is a laboratory instrument used in order to eliminate or recover solvents at low pressure, thus allowing the extraction of compounds more efficiently than with common distillation-condensation systems.
Laboratory homogenizer: What are the different types that exist?

These equipments allow obtaining nanoparticles, nano dispersions, nano emulsions and cell rupture at high pressure. It is widely used in laboratories as it facilitates testing with small amounts of sample and ensures quality results; this procedure is a very common step in the preparation of biological samples before analysis of nucleic acids and proteins, or the study of cells, metabolism, pathogens and many other targets.
CO2 zero emission plan for 2030

There is currently no country or region in the world that has not experienced the dramatic effects of climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions have increased considerably over the past 100 years, leading to an accelerated increase in global warming, which in turn has led to permanent changes in the climate system, the consequences of which may become irreversible if the necessary measures are not taken now.
What is the importance of an electroscalpel?
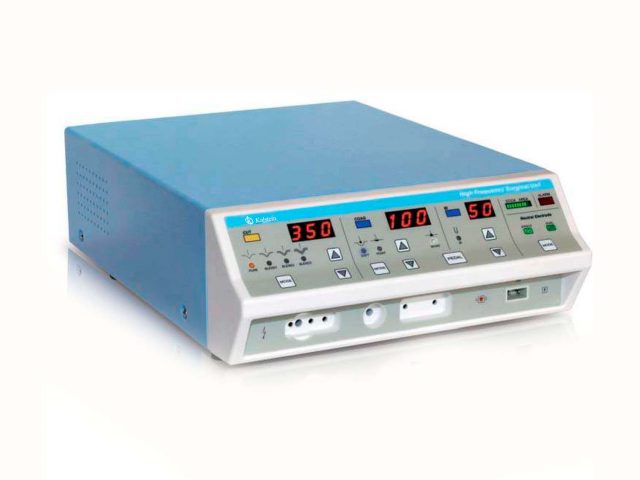

An electroscalpel is a medical device of electrical origin used in operating rooms with the aim of cutting or coagulating tissues and cauterizing them at the same time, thus reducing the time of surgical intervention and thus avoiding unwanted and unexpected bleeding. It is also known as an electric scalpel or surgical unit, and is commonly used today in many specialties of medicine, such as obstetrics, dentistry, orthopedics, dermatology and veterinary medicine, to name a few.
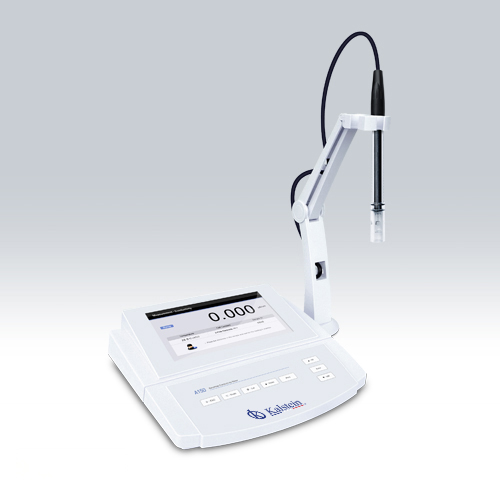
How does a laboratory ion meter work?
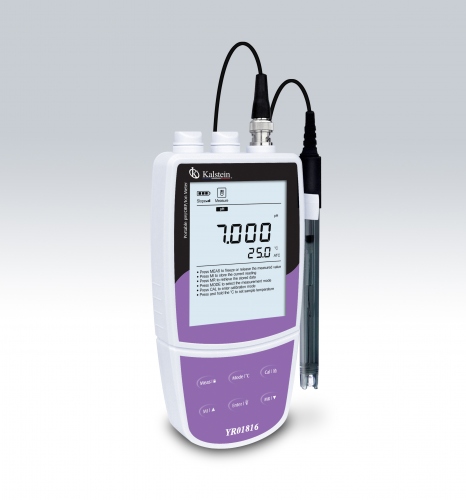

An ion meter is an analytical and electrochemical instrument used to measure the concentration of ions in a solution, using ion electrodes (ISE).
