Ph Meters
A pH meter consists of three essential parts: a pH measuring electrode, a reference electrode and a high input impedance meter. The reference electrode has a known, constant and stable potential.
The pH electrode can be considered as a battery, with a voltage that varies according to the pH of the measured solution. The pH-determining electrode is a hydrogen ion sensitive glass bulb, with a millivolt output that varies according to alterations in the relative concentration of hydrogen ions inside and outside the bulb. The output of the reference electrode does not change with the activity of hydrogen ions. The pH electrode has a very high internal resistance, which makes it difficult to measure voltage variation with pH. Therefore, the impedance of the pH meter input and the dispersion resistances are important factors.

Types of PH meters a Laboratory may need

Portable
• BNC connector is capable of connecting the different types of pH electrodes.
• 1 to 3 points calibration with auto-buffer recognition.
• Manual temperature compensation allows adjusting the temperature value.
• Auto-Read function senses and locks the measurement endpoint.
• Auto-Power Off effectively conserves battery life.
• Setup menu allows setting the pH buffer group, number of calibration points, temperature
unit, etc.
• Reset function automatically resumes all settings back to the factory defaults.
Table PH meters
- The economy benchtop pH meter is equipped with a white backlit LCD display.
- Automatic electrode slope display helps user decide if he wants to change the sensor.
- Automatic temperature compensation ensures accurate measurement, result.
- 2-point pushbutton calibration with buffer auto-recognition.
Accessories
- PH electrode
- The temperature probe (only for the PHS-3BW and PH-210 meter)
- PH buffer bags (pH4.01 / 7.00 / 10.01)
In Kalstein you can find the ideal PH Meters for your Laboratory

Pocket pH Meter – ° C / ° F YR01800
High-accuracy pocket pH meter, 1 to 3 points calibration, setup menu contains 5 options. The tester is suitable...

YR01803 Pocket pH / ° C / ° F Meter
High-accuracy pocket pH meter, 1 to 3 points calibration, setup menu contains 5 options. The tester is...
YR01822 Benchtop pH Meter
Classical benchtop pH meter, 1 to 3 points calibration, Automatic Temperature Compensation, setup menu contains 5 options...
YR01825 Benchtop pH / Ion Meter
Professional pH and ion meter, 2 to 5 points calibration, setup menu contains 20 options. The meter is suitable...
Our Best Selling PH Meters
Professional pH and ion meter, 2 to 5 points calibration, setup menu contains 20 options. The meter is suitable for measuring the pH, mV, ion concentration and water hardness.
• Professional pH/ion meter is equipped with a 7 inch TFT display.
• 1 to 5 points calibration with automatic recognition for USA, NIST and DIN buffers.
• Solution Temperature Coefficient compensates for the pure water samples and references
the pH to 25°C.
• 2 to 5 points calibration, including the 8 concentration points can be selected.
• Electrode management is capable of storing and recalling up to 3 electrode slopes.
• Selectable ion measurement methods (direct reading, known addition, known subtraction,
sample addition, sample subtraction) and concentration units (ppm, mg/L, mol/L, mmol/L).
| Model | YR01825 |
| pH | |
| Range | -2.000 to 20.000pH |
| Resolution | 0.001, 0.01pH, selectable |
| Accuracy | ±0.002pH |
| Calibration Points | 1 to 5 points |
| pH Buffer Options | USA, NIST, DIN, 5 custom buffers |
| ORP | |
| Range | ±2000.0mV |
| Resolution | 0.1mV |
| Accuracy | ±0.2mV |
| Calibration Points | 1 point |
| Measurement Modes | Relative or absolute mV |
| Ion Concentration | |
| Range | 0.001 to 30000 (deponding on the range of ISE) |
| Resolution | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1 |
| Accuracy | ±0.5% F.S. (monovalent), ±1% F.S. (divalent) |
| Calibration Points | 2 to 5 points |
| Calibration Solutions | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000 |
| Measurement Units | ppm, mg/L, mol/L, mmol/L |
| Measurement Methods | Direct reading, known addition, known subtraction, |
| sample addition, sample subtraction | |
| Water Hardness | |
| Range (Concentration) | 0.05 to 200mmol/L |
| Range (German Degree) | 0 to 1120°dH |
| Range (English Degree) | 0 to 1404°e |
| Range (French Degree) | 0 to 2000°fH |
| Range (Ca2+) | 0 to 8000mg/L |
| Range (CaCO3) | 0 to 19999mg/L |
| Range (CaO) | 0 to 11220mg/L |
| Resolution | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1 |
| Accuracy | ±1% F.S. |
| Calibration Points | 2 to 5 points |
| Calibration Solutions | 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100mmol/L |
| Temperature | |
| Range | 0 to 105°C/32 to 221°F |
| Resolution | 0.1°C/0.1°F |
| Accuracy | ±0.5°C/±0.9°F |
| Offset Calibration | 1 point |
| Calibration Range | Reading ±10°C |
| General Specifications | |
| Temperature Compensation | 0 to 100°C/32 to 212°F, manual or automatic |
| Stability Criteria | Standard or high-accuracy |
| Calibration Due Alarm | 1 to 31 days or off |
| Interval Readings | 10, 30, 60 seconds, 10, 30 minutes or off |
| Password Protection | 4 digits |
| Memory | Stores up to 1000 data sets |
| Output | USB communication interface |
| Connector | BNC, 3.5mm jack socket |
| Display | 7” TFT LCD |
| Power | DC12V, using AC adapter, 220V/50Hz |
| Dimensions | 240(L)×220(W)×80(H)mm |
| Weight | 1.7kg |
Analysis of the best Ph Meters for your Laboratory

How do I use a laboratory pH meter?
A pH meter or pH meter is a laboratory instrument used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution...

pH meter vs. dissolved oxygen meter
The pH is the unit of measurement that describes the degree of acidity or alkalinity and is measured on ...

Care and Calibration of your pH meter
A pH meter or pH meter is a scientific instrument that measures the activity of the hydrogen ion in aqueous ...
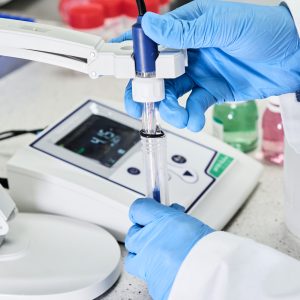
How does a pH meter work?
A pH meter or pH meter is an instrument used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The information provided by this equipment expresses...
Catalog of PH Meters models on offer
-

YR01822 Benchtop pH Meter
-

Benchtop pH / Ion Meter YR01826
-
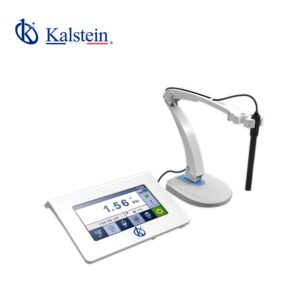
YR01825 Benchtop pH / Ion Meter
-
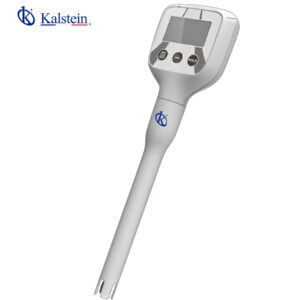
Pocket pH Meter – ° C / ° F YR01800 – YR01800-1
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

YR01823 Benchtop pH Meter
-

PH Meter YR01821
Guides to becoming an expert in PH Meters
PH Meter: Technology and accuracy
The measurement of pH (hydrogen potential) in the laboratory is one of the most important parameters that are...
What is PH and how is it measured?
pH is the unit of measurement that describes the degree of acidity or alkalinity and is measured on a scale that...
Importance of PH Meter
A pH meter is one of the most used equipment in a laboratory. It is used to measure the acidity or alkalinity...
Functions of PH Ion Meters in the Cosmetic Industry
In the manufacture of cosmetic products there are three essential aspects that must be addressed, the first, the elaboration of products pleasant to the touch and to the smell. The second is that they are efficient, that is, that these products improve...

Frequently Asked Questions about PH Meters
How to know the prices of PH Meters?
To know the price of pH Meters we invite you to send us an email with your request through the contact form...
What are the delivery times of the PH Meters?
- If the equipment of your interest is in stock or if it must be manufactured.
- The type of freight you have chosen, this may be; air or sea.
How to make a purchase of PH Meters?
- By email: [email protected]
- By telephone: +33 (0) 1 78 95 87 02
- E-commerce: Via Kalstein's official website in your country.
How does the warranty work?
Can I request a quote online?
Of course, you can request a quote for the Kalstein team of your interest, directly from our official website. Once you have identified your preferred model, click HERE
