KALSTEIN FRANCE
Find Your Equipment in
Seconds with AI + Chatgpt
Say goodbye to endless searching and doubts. With the power of ChatGPT, our AI helps you choose the ideal team with precise recommendations based on your specific needs. Try the tool now!
Delivery of the YR04986 water recirculator by an authorized distributor in Peru.

Limited time 25% discount on all pathology products

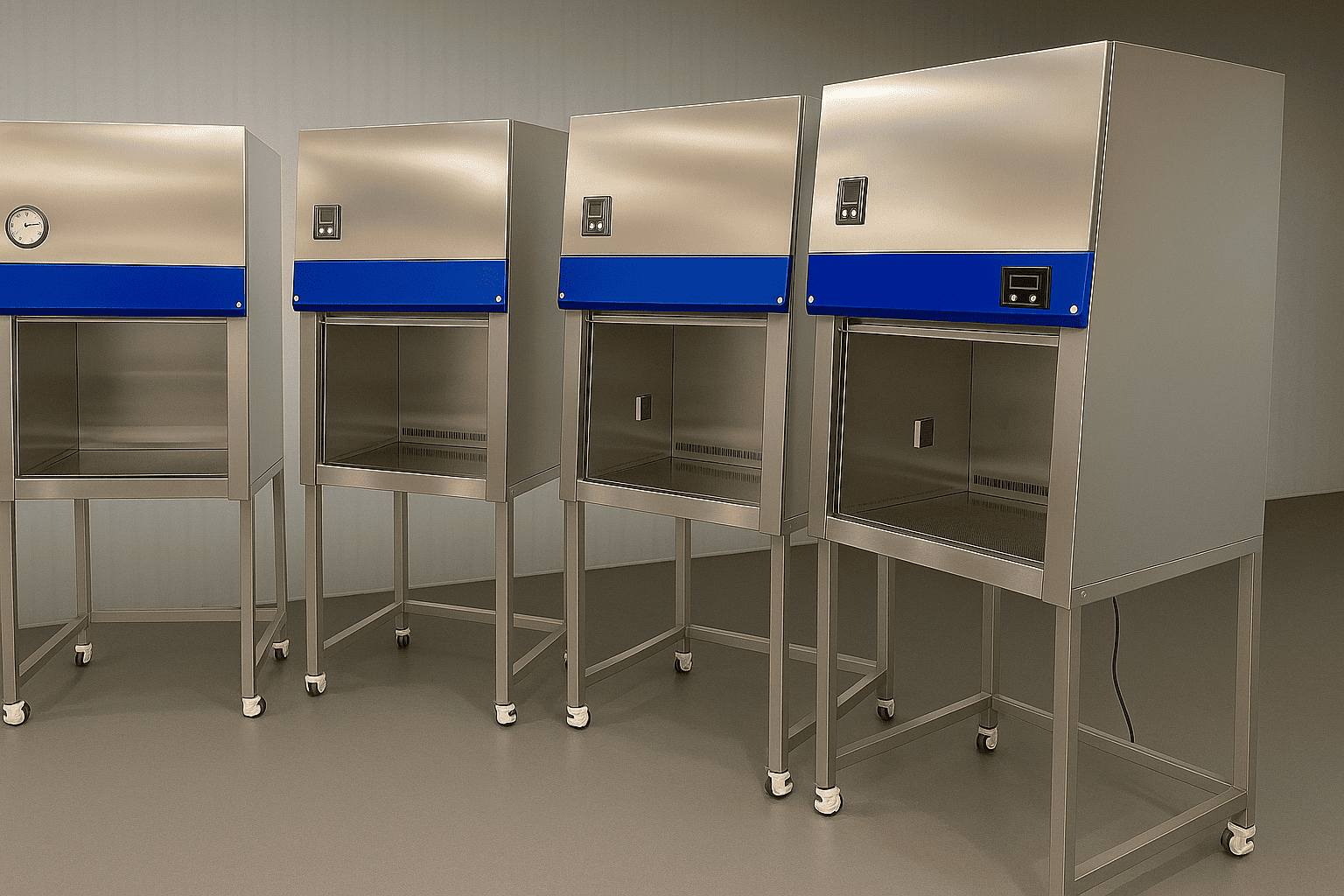
A2 biosafety cabinet, stainless steel, protects operator, product and environment.

MADE IN FRANCE 🇫🇷
The Excellence of French Savoir-Faire
At Kalstein France, we design and assemble our equipment in France to the strictest European standards. Each unit reflects our commitment to innovation, quality, and reliability.
years of manufacturing experience
- Applies to selected product lines.
- CE and EU certificates
- Quality control in France
- Commitment to our customers
- Team of experts trained in France
- French manufacturing, international reach
Yul Guzman
Founder and CEO
At Kalstein France, each piece of equipment undergoes a rigorous assembly and quality control process, ensuring compliance with European standards and reliability for our customers.
Made in France process
From assembly to certification
#01
Design and selection of components
Our experts select materials and components that meet European standards.
#02
Assembled in France
Each machine is assembled in our facilities to ensure optimal performance.
#03
Quality control
Strict testing is performed at every stage to ensure performance, safety, and reliability.
#04
Certification and Delivery
The equipment obtains CE certifications before being delivered to customers around the world.
Breaking news
1 New Insights into How the Brain Filters Expected Sounds: The Role of the Orbitofrontal Cortex 2
Understanding Sensory Filtering and Habituation Humans and animals alike have...
Read more1 Inflammation-Linked Protein Changes May Predict Post-Stroke Cognitive Decline 2
Introduction to the Study Researchers at The University of Manchester...
Read more1 Innovative Imaging Technique Offers New Insights for Type 1 Diabetes Treatment 2
Understanding the Role of Beta Cells in Type 1 Diabetes...
Read more1 Innovative MRI Technique Maps 3D Fluid Velocity in the Brain Without Contrast Agents 2
Introduction to Velocity Spectrum Imaging A groundbreaking MRI technique known...
Read more1 Does Having a History of Abortion or Miscarriage Influence Breast Cancer Risk? 2
Introduction A recent study published in the journal Acta Obstetricia...
Read more1 Exploring Multiscale Brain Modeling: Advances and Applications in Neuroscience 2
Introduction to Multiscale Brain Modeling Multiscale brain modeling represents one...
Read more1 Innovative Neural Implant Technique Promotes Skull Regrowth for Safe Brain Access 2
Introduction to the Breakthrough Neural Implant Technique A groundbreaking study...
Read more**Título Reformulado:** How Oncologists’ Psychological Health Affects Patient Care Quality
Introduction to the Study A comprehensive national study conducted in...
Read more1 Predicting Age-Related Cognitive Decline with Saliva Samples and AI 2
As individuals age beyond early adulthood, both physical and mental...
Read moreKalstein Breaking News
Nadia Kassou
The Trilingual Negotiator of Europe Originally from Barcelona, a Parisian...
Leer másKalstein Newsletter – Major Medical Equipment Project with Empirica in Ukraine
A Strategic Partnership to Enhance Healthcare Infrastructure in Eastern Europe...
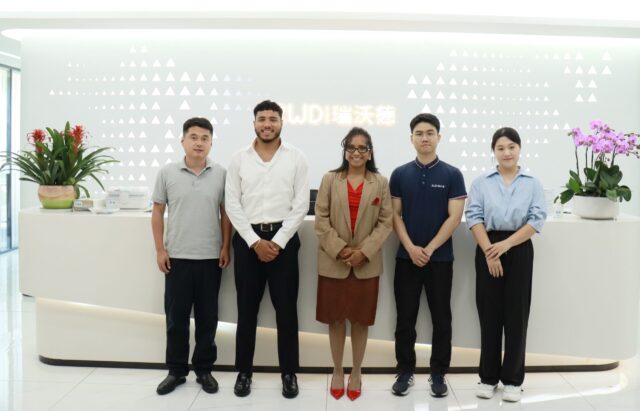
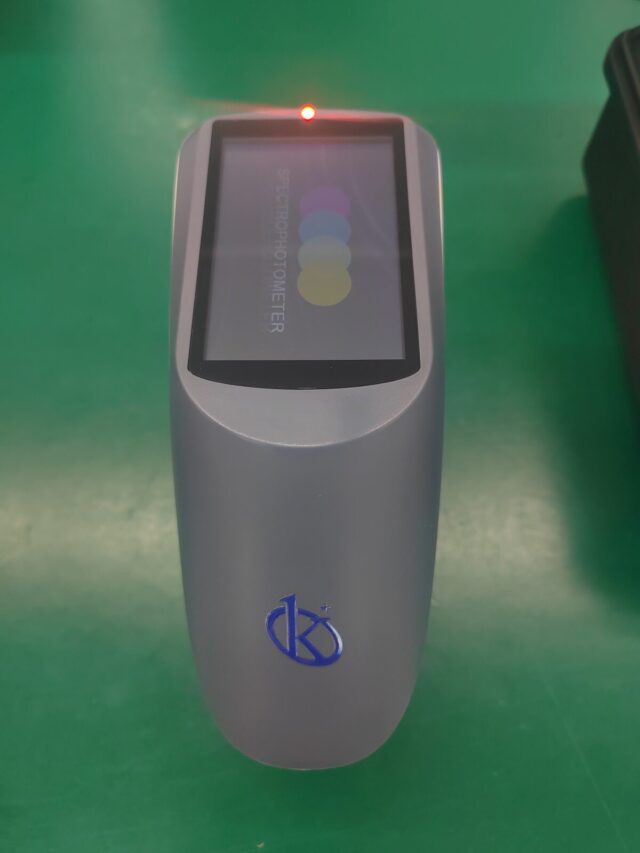
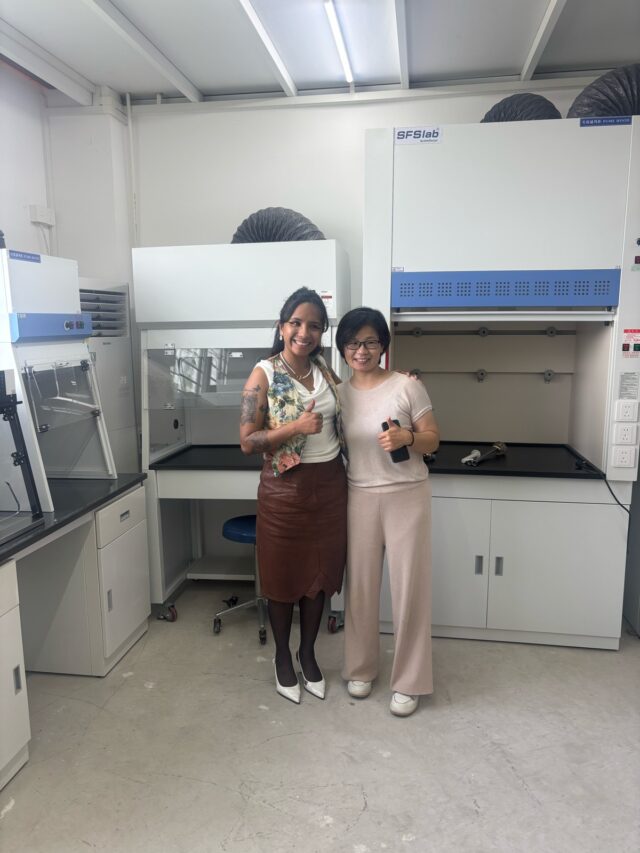
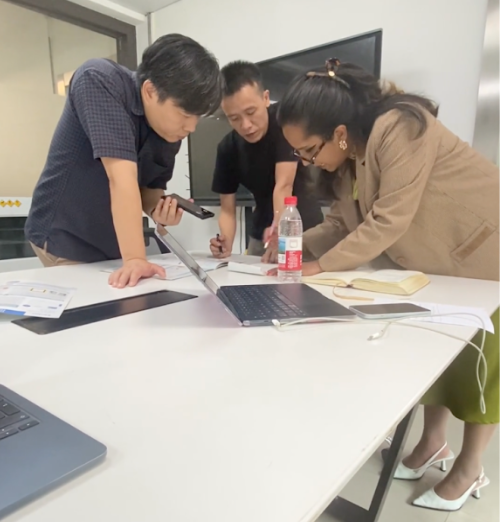
Leer másKalstein Newsletter – Special China Series | Episode 7/7
Kalstein in China – Meeting Excellence in Microbiological Safety Our...
Leer másKalstein Newsletter – Special Series China | Episode 5/7
Kalstein in China – Discovering Innovation in Service of Scientific...
Leer másKalstein Newsletter – New Agreement with DEMGY FAGARAS in Romania
A New Collaboration with a Key Client in Romania We...
Leer másKalstein Newsletter – Special China Series | Episode 4/7
Kalstein in China – A Strategic Partnership in the Field...
Leer másNewsletter Kalstein – Special China Series | Episode 3/7
Kalstein in China – A Business Journey at the Heart...
Leer másKalstein Supports Breast Cancer Awareness – Pink October 2025
🎗️ Pink October: A Month of Awareness and Solidarity On...
Leer másKalsteinVoices
Gente Kalstein – Episode 37 On this occasion, Gente Kalstein travels to the Faculty of Engineering at the Central University of Venezuela (UCV). There, the Guidance Service is developing the project “Ingenuity at the service of people with musculoskeletal disabilities”.
GenteKalstein – Épisode 36. This time, “Kalstein People” travels to Peru, where we have the opportunity to speak with Mr. José Alonso Cárdenas, CEO of Titanium and a business partner of the Kalstein family in the country.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 09 Meet Alpha Sow, founder and CEO of PrimeGear Maintenance. Entrepreneurship, local engagement, and innovation are at the core of his journey one that took him from Guinea to the United States, and ultimately to the creation of PrimeGear to address the technical needs of laboratories and medical facilities across Africa
GenteKalstein – Episode 34.
This time, we travelled to Ciudad Guayana, in eastern Venezuela. There, surgeon Luis Bartolozzi, together with a team of specialist doctors, successfully performed the first Bentall
GenteKalstein – Episode 32.
In this episode of Gente Kalstein, we travel to Chile, where we speak with nurse Odra Velásquez, who created a smart sandal that allows doctors to monitor a wide range of factors in patients suffering from diabetic foot.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 08 Meet Andris Djačenko, CEO of Laboveritas in Latvia. With a passion for science and a vision for automation, Andris has guided Laboveritas from its early days of research to becoming a key player in European laboratory innovation.
Kalstein Reportage: In this episode filmed in Paris, we explore the world of Marie Roussel, art therapist, and Valeria Serrano, a young Mexican woman supported in her journey through cancer.Through this intimate testimony, the report shows how art therapy becomes a space for expression and reconstruction.
GenteKalstein – Episode 32. This time, Gente Kalstein travels to the United States. We had a conversation with scientist Zulmary Manjarres about her research, which focuses on studying neuropathic pain as a predictor of Parkinson’s disease.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 7 Meet Andrea Ditzel and André Stocco, co-founders of BRASimp Equipamentos in Brazil. Two distinct careers converge to pursue one ambition: rethink how scientific equipment is brought to professionals across the country.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 05 In this new episode, discover the bold journey of Jamal Taqi, founder of TEKER, a young Moroccan company dedicated to scientific and laboratory equipment. With nearly twenty years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry, Jamal ventured into entrepreneurship to meet the growing demand for advanced technical solutions in Morocco.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 04 In this episode, meet Robert Nkala, who turned early setbacks into a remarkable entrepreneurial journey in the DRC’s scientific sector. From his first steps as a salesman to building a company in a challenging environment, Robert shares how he navigated local obstacles, seized new opportunities with the arrival of the internet, and forged international partnerships.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 03 In this episode, discover the remarkable journey of Abeda, a trailblazer in scientific sales in Pakistan. From her first major $1M contract to becoming a trusted leader in a male-dominated industry, Abeda shares how honesty, technical expertise, and relentless curiosity helped her earn the respect of clients and colleagues alike.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 02 In this second episode, meet A.K.M Faizur Rahman, one of the pioneers of animal probiotics in Bangladesh. Driven by a passion for microbiology and a desire to contribute to his country’s development, he chose to stay in Bangladesh and build innovative, science-based solutions from the ground up.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 01 In this first episode, meet Bichitra Biswas, a biomedical engineer turned entrepreneur. He shares his journey from working in hospitals to founding two innovative companies in the healthcare sector in Bangladesh.
Kalstein People is an interview project highlighting leaders and scientists associated with Kalstein, sharing their experiences and innovations in science and technology.
In this edition of Gente Kalstein we spoke with Nathalia Díaz Armas, a materials engineer from the Universidad Simón Bolívar (USB) in Caracas (Venezuela), about the advances in 3D printing and the possibilities that this technology offers to solve everyday problems in people’s homes. Díaz is currently completing a PhD in Plastics Engineering at the University of Lowell-Massachusetts (United States), specifically focusing her academic activity on achieving the printing of parts in rubber material.
We traveled to Kenya to learn the story of one of in the country: Mike Mbiti.
In this insightful conversation, Mr. Mbiti shares how his dream of pursuing science led him to found his own company in his home country.
Additionally, Mbiti provides details about the business model he has used over the past few years, leveraging another company he owns to help Cobi Advanced Technologies operate more effectively.
This time, we spoke with Manowar Hossain, representative of the company Neurone Engineering in Bangladesh.
Hossain describes what his work with the network of hospitals in his country is like, shares the challenges his company faced with the arrival of the Covid-19 pandemic, and talks about Neurone Engineering’s growth and expansion plans for the future.
In this interview, we spoke with Xochitl Rosas, founder of Labx Scientific in Mexico and a key collaborator of Kalstein, about the successful trajectory of her family business. Xochitl shares how Labx has thrived under her leadership, highlighting the majority participation of women in her team, a central aspect of her company culture.
On this occasion, from Caracas (Venezuela), we spoke with biologist María Alejandra Duarte about the work of one of the Jacinto Convit Foundation’s most important branches: the Molecular Diagnostic Unit (UDM).
On this occasion we spoke with the Venezuelan biologist Jeismar Carballo who, from Madrid and with the help of the Jacinto Convit Foundation, works every day on the development of a vaccine against breast cancer (ConvitVax).
KalsteinVoices
Gente Kalstein – Episode 37 On this occasion, Gente Kalstein travels to the Faculty of Engineering at the Central University of Venezuela (UCV). There, the Guidance Service is developing the project “Ingenuity at the service of people with musculoskeletal disabilities”.
GenteKalstein – Épisode 36. This time, “Kalstein People” travels to Peru, where we have the opportunity to speak with Mr. José Alonso Cárdenas, CEO of Titanium and a business partner of the Kalstein family in the country.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 09 Meet Alpha Sow, founder and CEO of PrimeGear Maintenance. Entrepreneurship, local engagement, and innovation are at the core of his journey one that took him from Guinea to the United States, and ultimately to the creation of PrimeGear to address the technical needs of laboratories and medical facilities across Africa.
GenteKalstein – Episode 34.
This time, we travelled to Ciudad Guayana, in eastern Venezuela. There, surgeon Luis Bartolozzi, together with a team of specialist doctors, successfully performed the first Bentall
GenteKalstein – Episode 33.
In this episode of Gente Kalstein, we travel to Chile, where we speak with nurse Odra Velásquez, who created a smart sandal that allows doctors to monitor a wide range of factors in patients suffering from diabetic foot.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 08 Meet Andris Djačenko, CEO of Laboveritas in Latvia. With a passion for science and a vision for automation, Andris has guided Laboveritas from its early days of research to becoming a key player in European laboratory innovation.
Kalstein Reportage: In this episode filmed in Paris, we explore the world of Marie Roussel, art therapist, and Valeria Serrano, a young Mexican woman supported in her journey through cancer. Through this intimate testimony, the report shows how art therapy becomes a space for expression and reconstruction.
GenteKalstein – Episode 32. This time, Gente Kalstein travels to the United States. We had a conversation with scientist Zulmary Manjarres about her research, which focuses on studying neuropathic pain as a predictor of Parkinson’s disease.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 7 Meet Andrea Ditzel and André Stocco, co-founders of BRASimp Equipamentos in Brazil. Two distinct careers converge to pursue one ambition: rethink how scientific equipment is brought to professionals across the country.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 05 In this new episode, discover the bold journey of Jamal Taqi, founder of TEKER, a young Moroccan company dedicated to scientific and laboratory equipment. With nearly twenty years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry, Jamal ventured into entrepreneurship to meet the growing demand for advanced technical solutions in Morocco.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 04 In this episode, meet Robert Nkala, who turned early setbacks into a remarkable entrepreneurial journey in the DRC’s scientific sector. From his first steps as a salesman to building a company in a challenging environment, Robert shares how he navigated local obstacles, seized new opportunities with the arrival of the internet, and forged international partnerships.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 03 In this episode, discover the remarkable journey of Abeda, a trailblazer in scientific sales in Pakistan. From her first major $1M contract to becoming a trusted leader in a male-dominated industry, Abeda shares how honesty, technical expertise, and relentless curiosity helped her earn the respect of clients and colleagues alike.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 02 In this second episode, meet A.K.M Faizur Rahman, one of the pioneers of animal probiotics in Bangladesh. Driven by a passion for microbiology and a desire to contribute to his country’s development, he chose to stay in Bangladesh and build innovative, science-based solutions from the ground up.
Kalstein Voices – Episode 01 In this first episode, meet Bichitra Biswas, a biomedical engineer turned entrepreneur. He shares his journey from working in hospitals to founding two innovative companies in the healthcare sector in Bangladesh.
Kalstein People is an interview project highlighting leaders and scientists associated with Kalstein, sharing their experiences and innovations in science and technology.
On this occasion, from Caracas (Venezuela), we spoke with biologist María Alejandra Duarte about the work of one of the Jacinto Convit Foundation’s most important branches: the Molecular Diagnostic Unit (UDM).
In this interview, we spoke with Xochitl Rosas, founder of Labx Scientific in Mexico and a key collaborator of Kalstein, about the successful trajectory of her family business. Xochitl shares how Labx has thrived under her leadership, highlighting the majority participation of women in her team, a central aspect of her company culture.
Discover Kalstein Plus
The transformation of the medical and scientific sector
Connect, discover, buy, sell and grow.
- Interconnection
- Trust
- Learning
- Workflow
Optimización del flujo de información
From quote to delivery, we make every step smoother and more efficient.
- Tender preparation (with template recommendations)
- Customs cost estimate (from origin to destination)
- Shipping cost estimate (for all types of transportation)
- Delivery schedules (including manufacturing time and transit time)
- Location of laboratories, consulting rooms, local distributors, local technical service, and international manufacturers.
You have doubts? We answer all your questions
Why choose Kalstein Plus?

Save time with automatic quotes
Do you need to strengthen your cash flow? Kalstein Type I Loan
Receiving and preparing the order for your company, with shipping to the end customer.
About all types of Kalstein shipments
Support for distributors in bidding processes
Integrated Networks
Interact and collaborate with profiles from end users to manufacturers.
Variety of Prices
Gain access to a range of plans with different prices and durations.
Exact Location
Accurately find local manufacturers, local technical support and local distributors.
Kalstein Verification
Trust in products and services thanks to compliance with international quality standards.
Integrated Networks
Interact and collaborate with profiles from end users to manufacturers.
Variety of Prices
Gain access to a range of plans with different prices and durations.
Exact Location
Accurately find local manufacturers, local technical support and local distributors.
Kalstein Verification
Trust in products and services thanks to compliance with international quality standards.
Together with our authorized partners, we bring quality solutions
to professionals around the world.


HOW WE CAN HELP YOU
Sectors and categories
We offer state-of-the-art and advanced solutions for a wide range of sectors including medical, laboratory, dental, furniture, and rehabilitation. With a strong commitment to innovation and excellence in customer service, we strive to provide efficient and effective solutions to meet the needs of each of our clients.
Scientific sector
Laboratory
We offer over 30 product lines for the laboratory sector. We provide innovative solutions, cutting-edge equipment, and personalized technical support. We work with the highest quality and efficiency, always focused on meeting the changing needs of the sector.
Download catalogs
We offer a range of educational resources, including informative catalogs, videos, webinars, and more.
Medical sector
Health
Wide variety of medical sector lines. We offer innovative and high-quality solutions to improve efficiency and patient well-being. Explore our section and discover how we can help you achieve your medical goals with our products.
We offer a range of educational resources, including informative catalogs, videos, webinars, and more.
Download catalogs
Contact us to know prices, logistics and delivery times.

Chemical sector
Reagents and Consumables
Discover Kalstein’s exclusive line of reagents and consumables, meticulously designed to meet the demanding precision and quality needs of laboratories around the world. Our portfolio covers a wide range of essential products, from high-purity reagents to durable laboratory consumables, ensuring that every test and analysis is performed with maximum reliability and efficiency.
We offer a range of educational resources, including informative catalogs, videos, webinars, and more.
Download catalogs

Furniture sector
Furniture
Explore our distinguished line of Kalstein furniture, specially designed to meet the high demands of functionality and style in laboratory environments. Our selection ranges from robust, durable work tables to ergonomic chairs and cabinets, all created to facilitate productivity and comfort in the laboratory. We encourage you to discover how our furniture solutions can transform your workspace and optimize each task.
We offer a range of educational resources, including informative catalogs, videos, webinars, and more.
Download catalogs
Want to be a distribuidor for the Kalstein brand?
Explore our membership plans and all the benefits we offer you
Dental sector
Dentistry
We offer a range of educational resources, including informative catalogs, videos, webinars, and more.
Download catalogs
Veterinary Sector
Veterinary
Kalstein’s specialized line of veterinary equipment is designed to meet the needs for efficiency and comfort in veterinary clinics and hospitals. Each product in the range has been developed with the highest technology and functional design, ensuring durability and ease of handling, allowing veterinary professionals to offer high quality and precision care.
Download catalogs
We offer a range of educational resources, including informative catalogs, videos, webinars, and more.
Do you have a question?
Find us – Call us
+33 9 83 04 38 83

Informative articles and news
KALSTEIN UP TO DATE
Latest articles, events and videos.
Stay on top of scientific advances: up-to-date news, expert advice, practical recommendations and interesting events to keep you informed and at the forefront of the scientific sector.
1 New Insights into How the Brain Filters Expected Sounds: The Role of the Orbitofrontal Cortex 2
Understanding Sensory Filtering and Habituation Humans and animals alike have developed the ability to discern which sounds or sensory cues...
Innovative Solutions: Comparing Industrial 10L Magnetic Stirrers
When it comes to laboratory equipment, the Industrial 10L Hotplate Magnetic Stirrer Bar With Heating YR02939 by Kalstein and the...
1 Inflammation-Linked Protein Changes May Predict Post-Stroke Cognitive Decline 2
Introduction to the Study Researchers at The University of Manchester have uncovered a potential method to predict cognitive impairment following...