The spectrophotometer
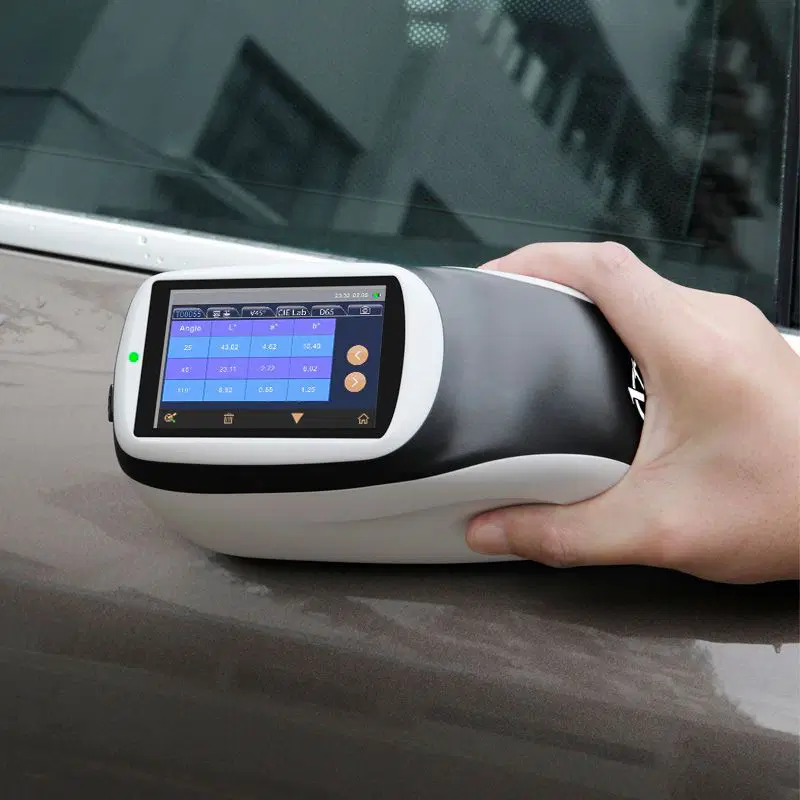

A spectrophotometer is an instrument that measures how much light a substance absorbs. Measures the amount of photon absorbance after passing through a solution. Each substance transmits, reflects, and absorbs light slightly differently. In chemistry, spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of the transmission properties of a material based on the light wave.
Ultracentrifuge: rpm and gravity

The ultracentrifuge is an equipment intended for the separation of particles with a low sedimentation coefficient (microsomes, viruses, macromolecules). The maximum speed it reaches is 100,000 rpm or 802,000 xg, so it has auxiliary cooling and high vacuum systems.
Laboratory micropipettes

A micropipette is a laboratory device used to absorb and transfer small volumes of liquids. The volumes that can be captured by these instruments vary according to the model and type of pipette: the most common, called p20, p200 and p1000, admit a maximum of 20, 200 and 1000 μl, respectively.
What is a vortex shaker?
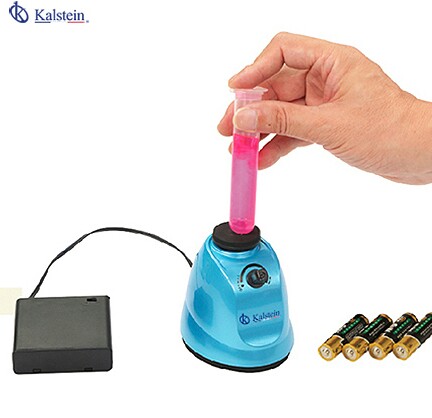

A vortex shaker is a simple device commonly used in laboratories to mix small vials of liquid. It consists of an electric motor with a vertically oriented drive shaft attached to a slightly mounted recessed rubber part.
What is pathological anatomy?

Pathological anatomy is the science that studies the pathophysiological and morphological alterations of the disease. It studies the disease at an organic, tissue, cellular, subcellular, and molecular level.
Electrophoresis and Gel Documentation Systems

Gel electrophoresis is a widely used technique in life science laboratories to separate macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. In this technique, molecules are separated according to size and electrical charge.
What is a cryostat?

The cryostat is a piece of equipment used in the processing of samples for histological or histopathological diagnosis or identification. It is mainly used to freeze and obtain frozen tissue sections or samples that have not been previously fixed by chemical methods, to avoid losing some important characteristics necessary for observation.
Main applications of a CO2 incubator

A CO2 incubator is a laboratory equipment also called a gasification incubator, where the development of cell and tissue cultures is guaranteed by creating a natural atmosphere. This culture of living organisms in vitro is one of the main applications of CO2 incubators. That is why these devices are used mainly in medical research and in the pharmaceutical industry in:
Centrifugation: RPM vs. G Force
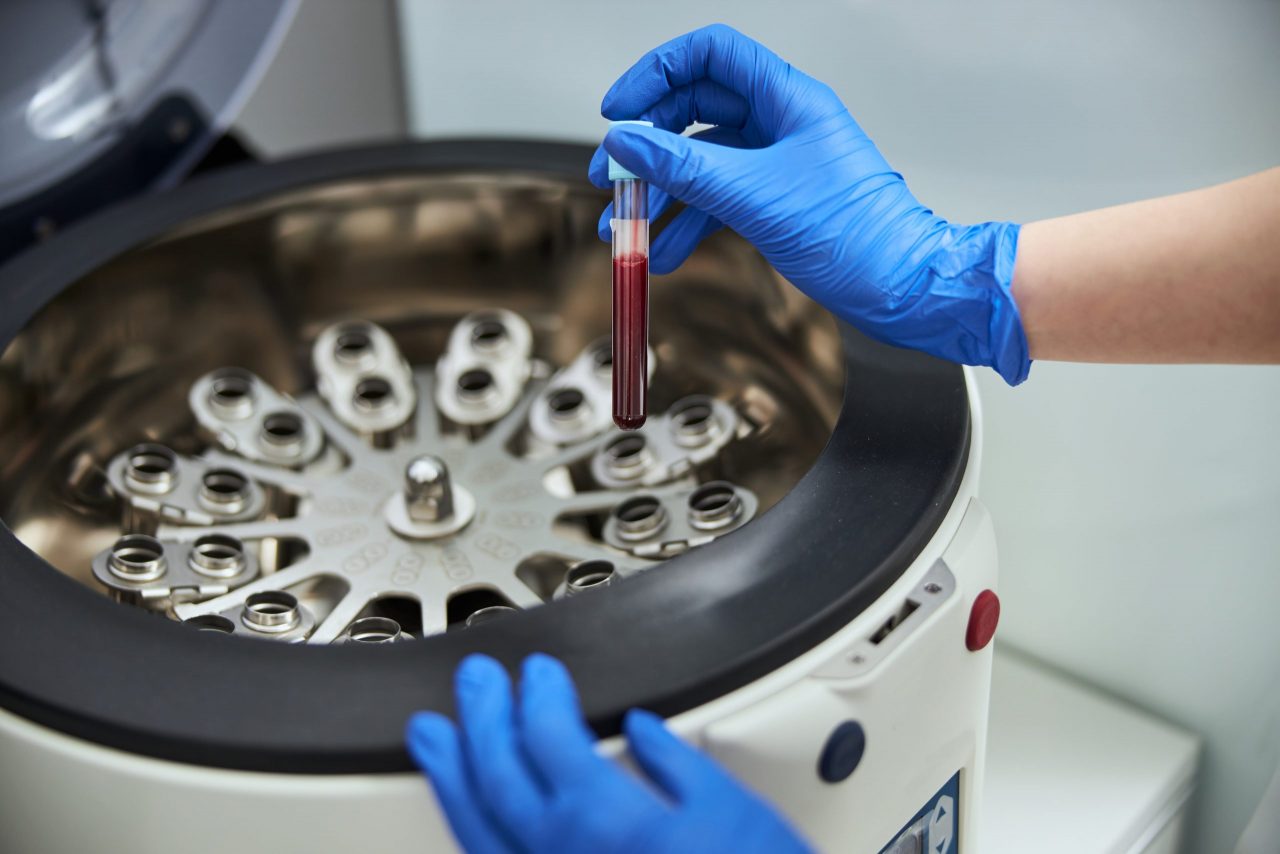
Centrifugation is one of the most important and widely applied research techniques in biochemistry, cell and molecular biology, and medicine. Today’s research and clinical applications depend on the isolation of cells, subcellular organelles, and macromolecules, generally high throughput. A centrifuge uses centrifugal force (g-force) to isolate suspended particles from the surrounding medium either in batches or as a continuous flow.
Incubators, their application in cell and microbiological cultures

An incubator is a laboratory equipment that is used to maintain and grow microbiological cultures or cell cultures, regulating viable growth factors such as temperature, humidity and ventilation.
