Comparative Analysis: Manual Wheelchair YR05456 vs Wheelchair Breezy 250
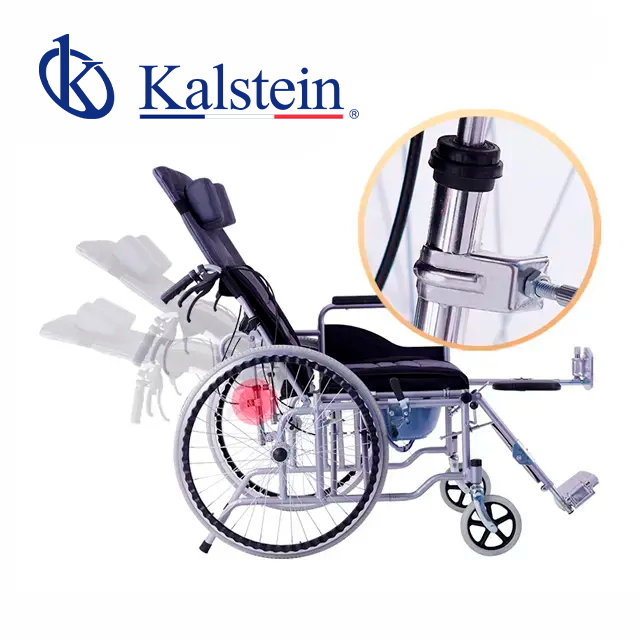

When it comes to selecting the right manual wheelchair, the options available in the market are abundant. Two contenders that stand out are the Manual Wheelchair YR05456 by Kalstein and the Wheelchair Breezy 250 by Sunrise Medical. Each of these products offers unique features designed to enhance user comfort and mobility. The Manual Wheelchair YR05456 […]
The Ultimate Guide to Veterinary Monitors by Kalstein: Features, Comparisons, and Benefits
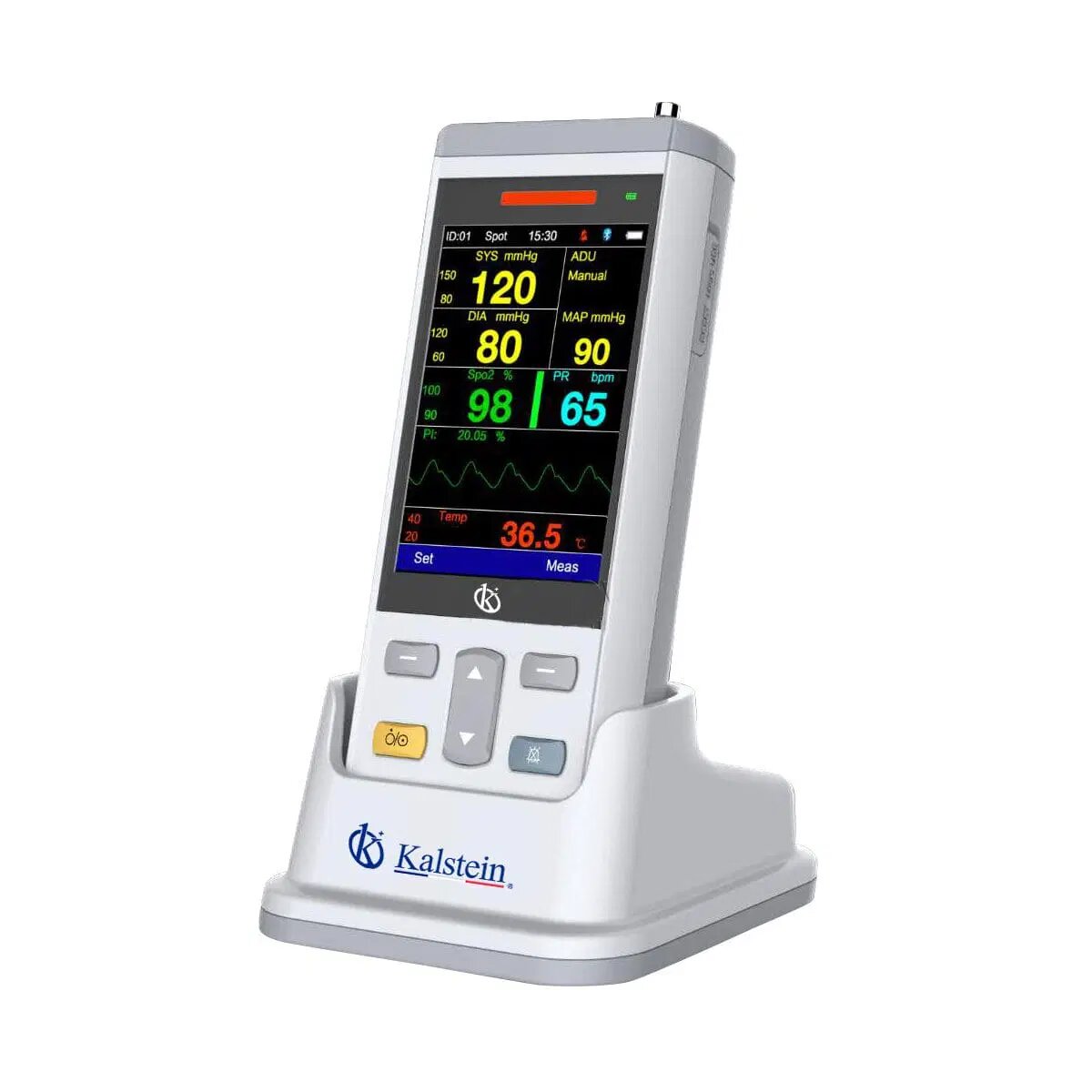
Veterinary Monitor, Brand Kalstein As someone who has dedicated time using and understanding veterinary monitors, I can confidently say that the veterinary monitors from Kalstein stand out remarkably in the market. With an extensive background in providing reliable medical equipment, Kalstein has carved a niche for itself, especially in the veterinary sector. These monitors are […]
Advanced Industrial Tumble Dryers: Comparing Kalstein and UniMac

Industrial dryers play a critical role in both small and large-scale laundry operations. Choosing the right equipment can make a significant difference in efficiency and product longevity. Here, we will compare two notable products in the industrial tumble dryer market: the 100KG Tumble Dryer (Full Stainless Steel) YR06326 by Kalstein, and the Industrial Tumble Dryer […]
Scientific Innovation: Comparing Kalstein’s Mini Vortex Mixer with VWR’s VXMN

In modern laboratory settings, efficiency and precision are key. The Mini Vortex Mixer – YR06042 – YR06043 by Kalstein embodies these principles with its state-of-the-art design and robust functionality. This vortex mixer is designed to blend small vials of liquids with a turbulent spinning motion, ensuring uniform mixing. Kalstein’s model stands out due to its […]
Dialyzer Reprocessing Machine YR06375 vs Dialyzer Reprocessing System 100: A Comprehensive Comparison

In the world of dialysis, the selection of a reliable dialyzer reprocessing machine is crucial for both the safety of patients and the efficiency of healthcare providers. Today, we compare two leading products in this category: the Dialyzer Reprocessing Machine YR06375 by Kalstein and the Dialyzer Reprocessing System 100 by MEDIVATORS. Both machines aim to […]
Revolutionizing Veterinary Dentistry: Unveiling the Advanced Features of Veterinary Dental Units
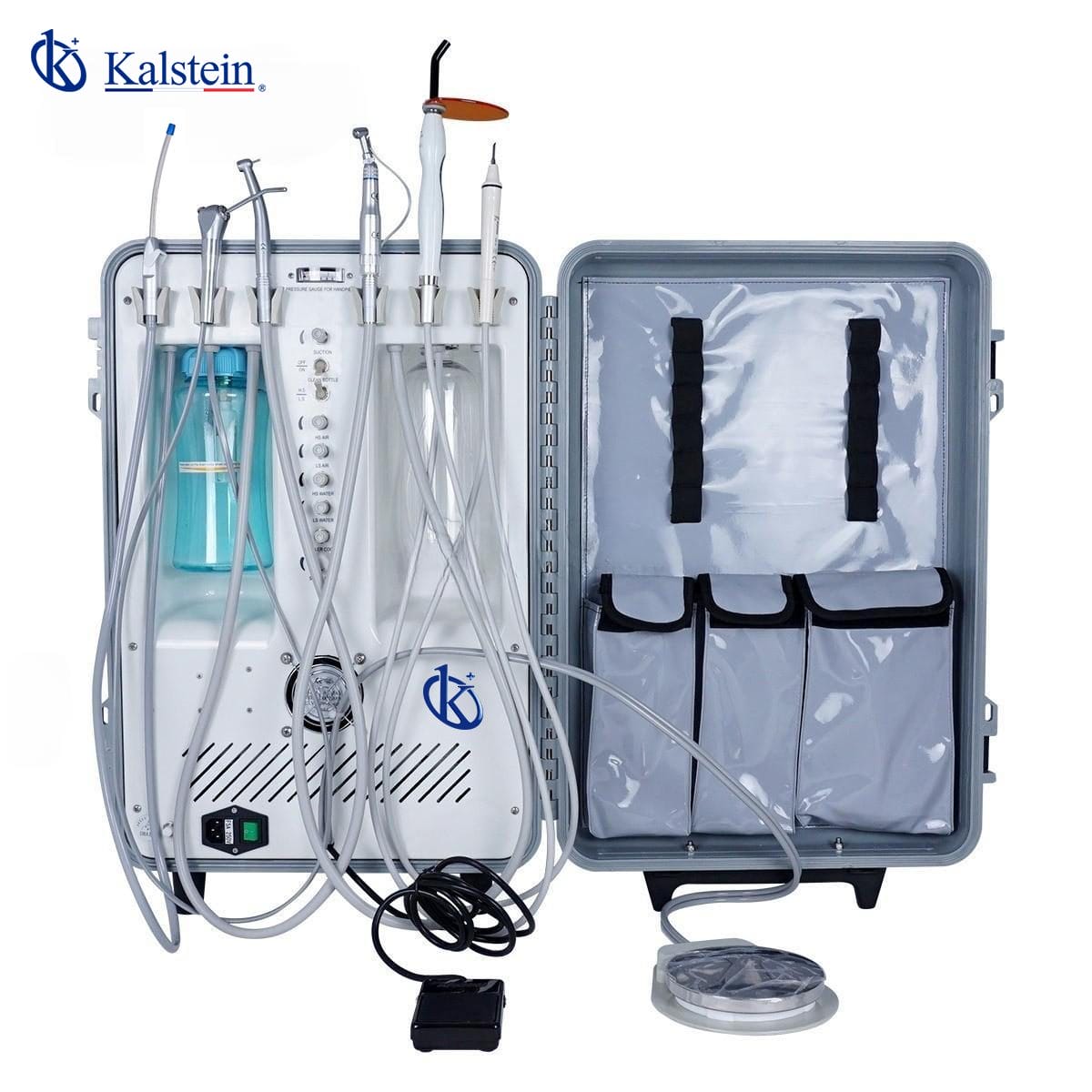
Veterinary Dental Unit: Brand Kalstein I’ve been fortunate to explore various veterinary dental equipment and among the top tiers, Kolstein’s Veterinary Dental Units stand tall. Kalstein has established a reputation for delivering high-quality medical devices and their dental units for veterinary purposes are no exception. Known for their precision and innovation, these units are designed […]
The Ultimate Guide to Medical Transfer Stretchers: Efficiency, Quality, and Innovation
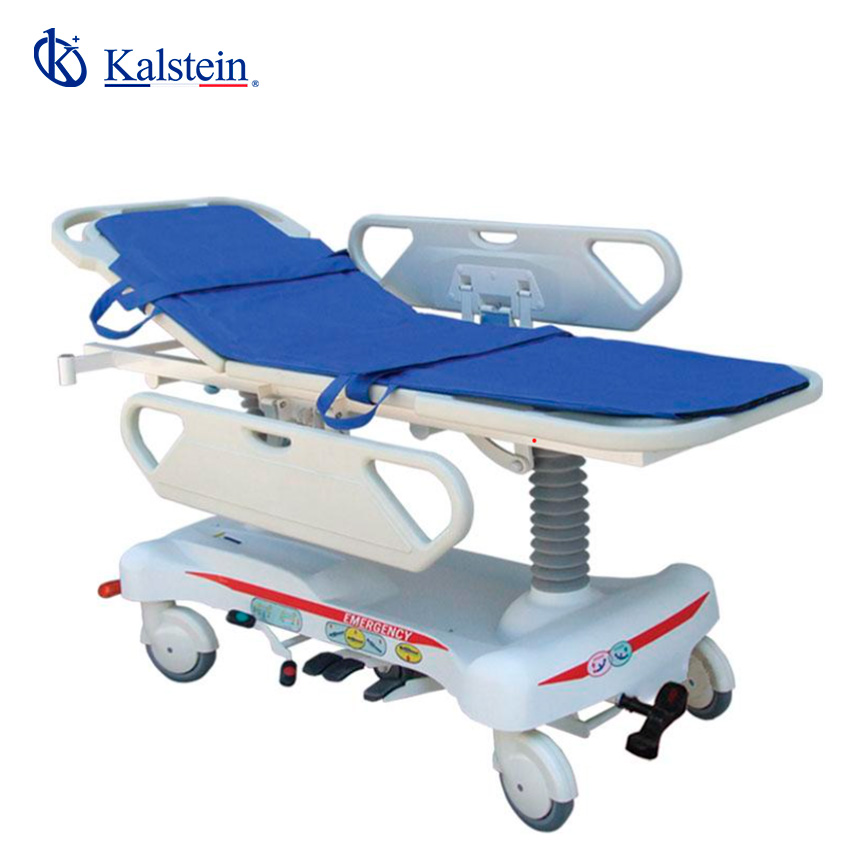
Medical Transfer Stretcher by Kalstein Having personally tried various patient transfer stretchers, I was particularly impressed by the ones from Kalstein. Their design precision and commitment to providing quality service are evident in their range, making these stretchers a popular choice in medical facilities. From my experience, Kalstein excels in offering solutions that meet stringent […]
Discover the Power of Precision with Kalstein Viscometers
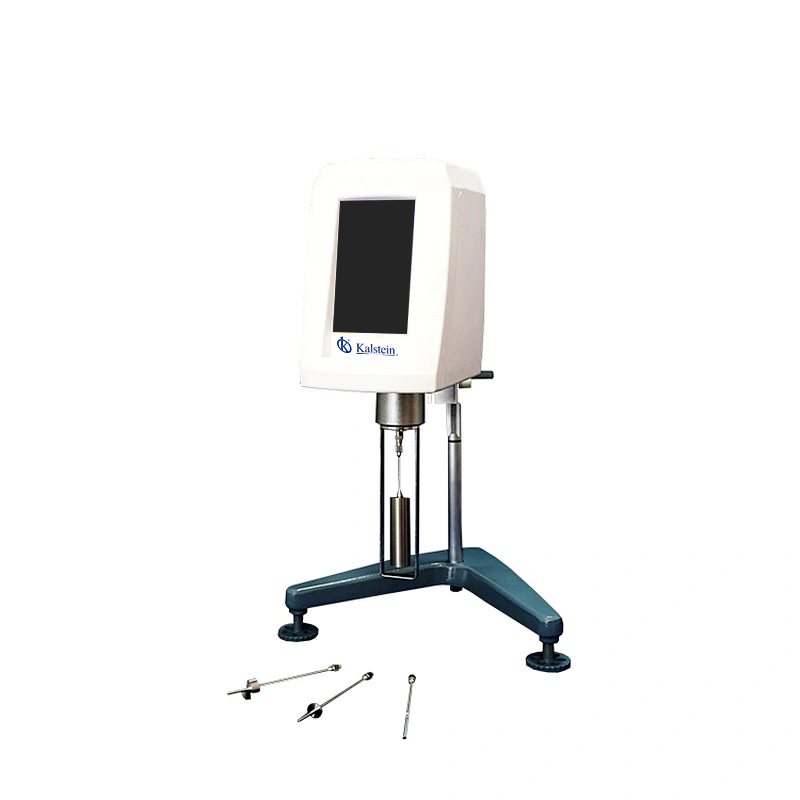

Kalstein Viscometers: High Accuracy and Reliability Kalstein’s viscometers are designed with precision and reliability in mind, offering unparalleled performance for laboratory needs. As someone who has used these instruments extensively, I can assert that these viscometers provide accurate viscosity measurements, essential for a wide range of applications in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to petrochemicals. The […]
Innovative Gynecological Examination Tables: Kalstein YR06278 vs. MedGyn MT-300
When it comes to gynecological examination tables, two products stand out in the medical field: the Gynecological Examination Table YR06278 from the reputable brand Kalstein and the Examination Table MT-300 from MedGyn. These two tables, while serving similar functions, present different features and capabilities that might suit varying needs of medical professionals. The Kalstein Gynecological […]
BenchTop Freeze Dryers: A Comparative Guide Between Kalstein and Labconco

Freeze drying, a critical process in many scientific and industrial applications, requires reliable equipment to ensure optimal results. Two popular choices in this field are the Benchtop Normal Lab Freeze Dryer YR05186 from Kalstein and the FreeZone Benchtop Freeze Dry System from Labconco. Each offers unique features tailored to address varying needs in precision, efficiency, […]
