Cutting-Edge Precision: A Comparative Look at Kalstein’s YR05568 // YR05572 vs Mettler Toledo XPR Analytical Balances
In the demanding field of laboratory measurements, precision is key. Analytical balances with internal calibration capabilities are essential tools that ensure accuracy in your measurements. Today, we delve into a detailed comparison of two leading products in this domain: the Internal Calibration Analytical Balance YR05568 // YR05572 by Kalstein, and the Analytical Balance XPR (Internal […]
Revolutionize Your Pet Care with Kalstein’s Veterinary Grooming Clipper
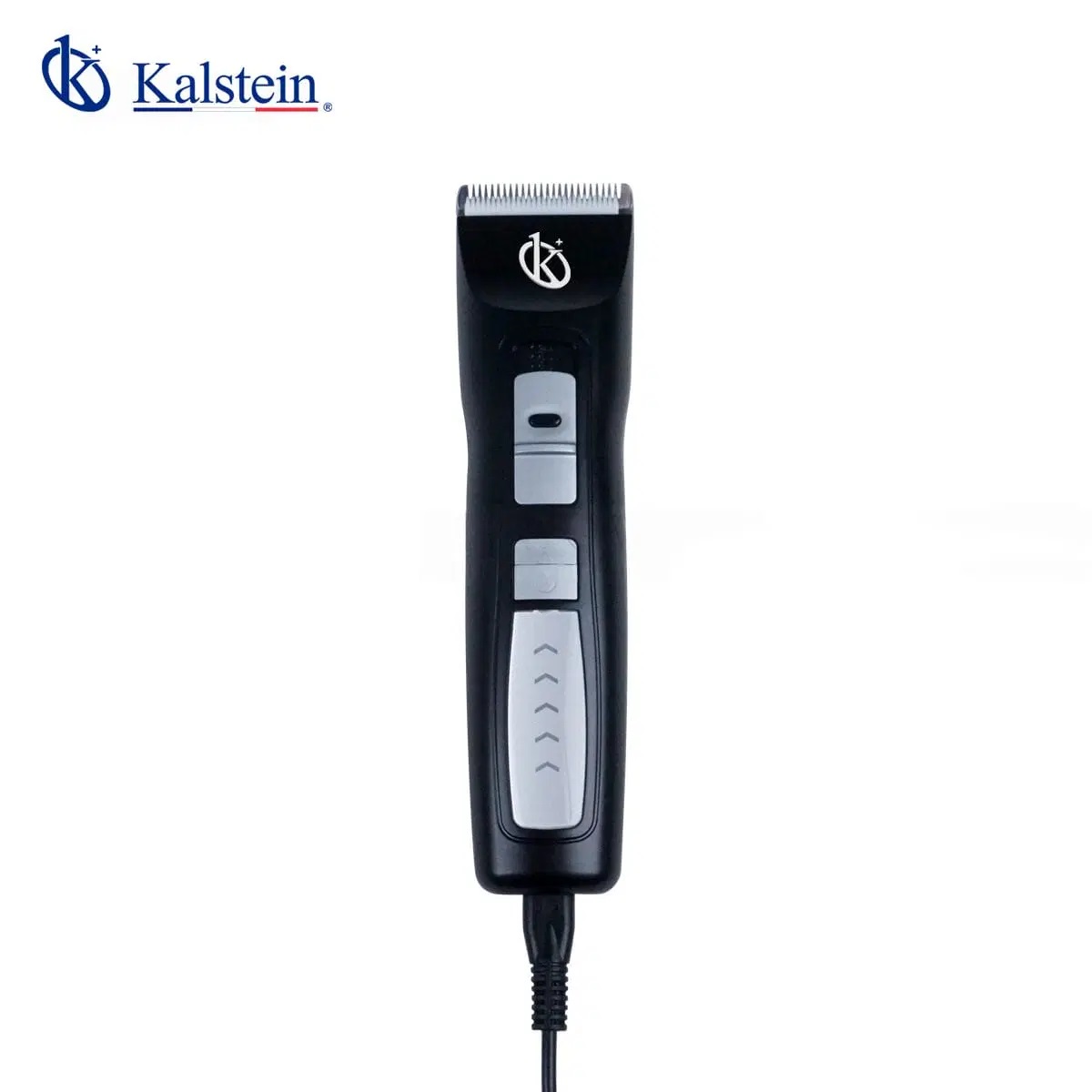

Veterinary Grooming Clipper, Brand Kalstein When it comes to pet grooming, serious professionals know the importance of using top-quality tools. That’s where the Veterinary Grooming Clipper from Kalstein shines. Based on extensive customer feedback, I’ve learned that users appreciate the precision and reliability this product brings to their grooming tasks. It’s the kind of tool […]
Discover the Power of Oxygen: A Comprehensive Look at Kalstein’s Oxygen Concentrators

Oxygen Concentrator, Kalstein Brand Having firsthand experience with Kalstein’s Oxygen Concentrators, I can confidently say that these devices stand out in the medical field for their efficiency and reliability. As a leading brand in the healthcare sector, Kalstein has been at the forefront of providing cutting-edge medical equipment, and their Oxygen Concentrators are no exception. […]
The Ultimate Guide to Class II Biosafety Cabinets: Safety and Innovation with Kalstein
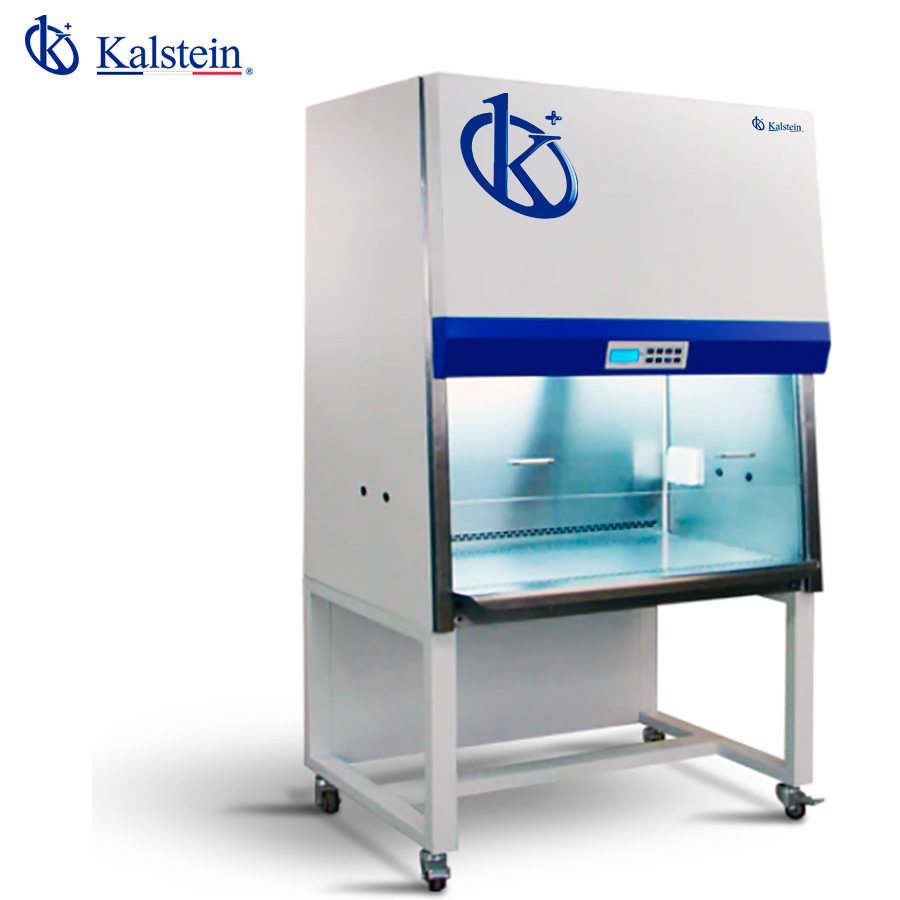

Class II Biosafety Cabinets, Kalstein Brand Kalstein, a renowned name in laboratory equipment, offers Class II Biosafety Cabinets that set the benchmark for laboratory safety and efficiency. As someone who has closely worked with these cabinets, I can vouch for their superior quality and innovation. The meticulous design and robust construction make them an essential […]
Comparing Rotary Evaporators: Kalstein YR02306 vs. Heidolph Hei-VAP Precision
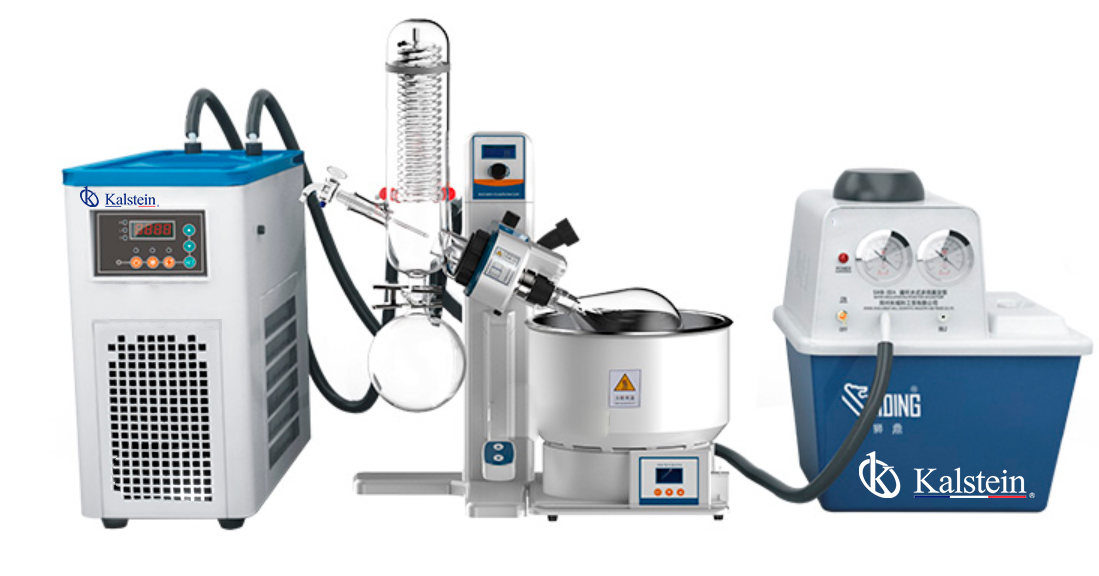

When choosing a rotary evaporator for your laboratory needs, two leading options that often come to the fore are the Kalstein Rotary Evaporator YR02306 and the Heidolph Hei-VAP Precision Rotary Evaporator. Both offerings promise efficiency, reliability, and innovative features that cater to various scientific applications. The Kalstein Rotary Evaporator YR02306 stands out with its advanced […]
Comprehensive Comparison: Full-Auto Hematology Analyzer YR05121 vs. Hematology Analyzer XN-550
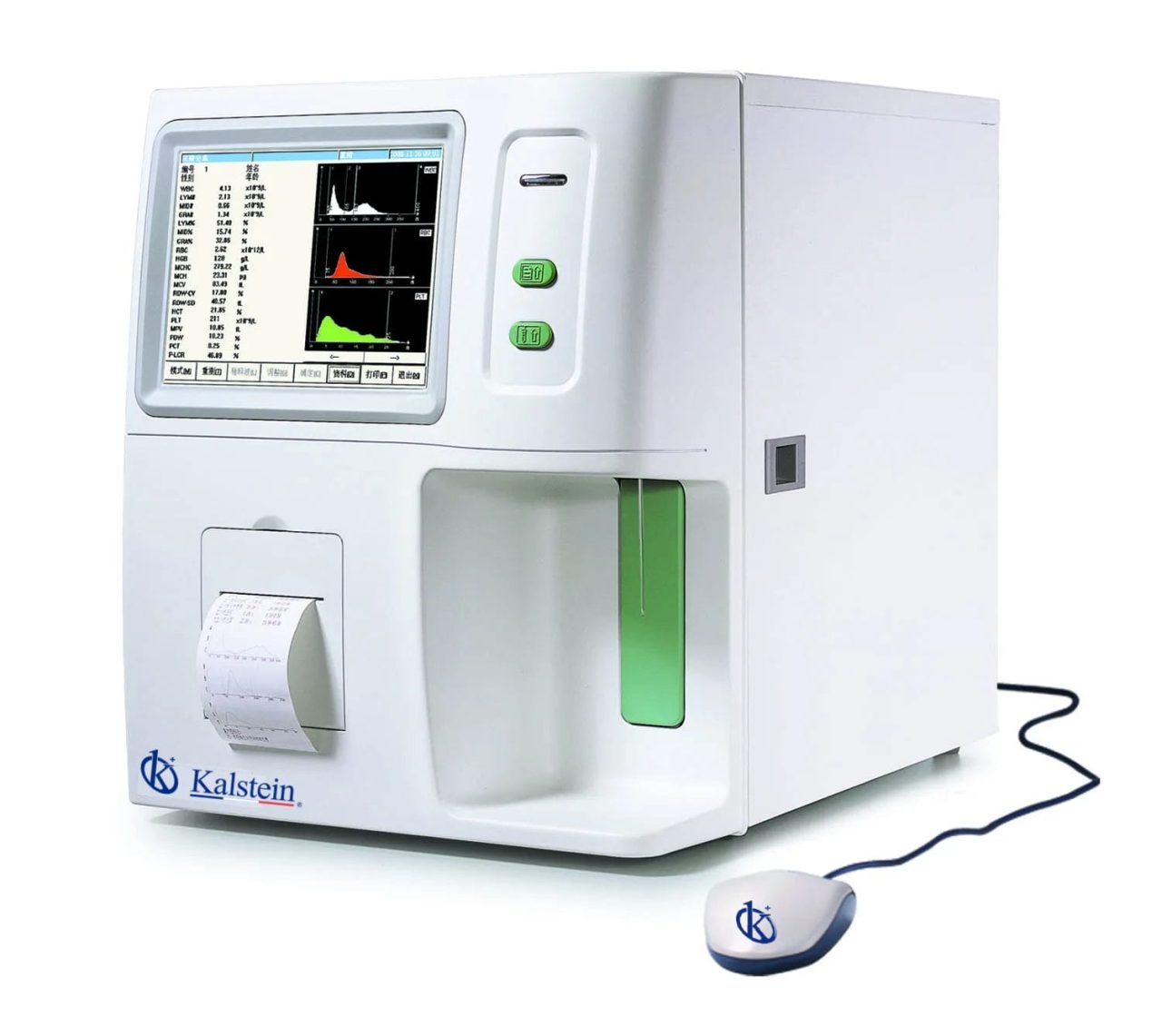
When it comes to hematology analyzers, precision and reliability are crucial components for laboratory efficiency. In this comparative analysis, we will explore the features, functionalities, and benefits of the Full-Auto Hematology Analyzer YR05121 by Kalstein and the Hematology Analyzer XN-550 by Sysmex. Both are technologically advanced products designed to facilitate the most accurate blood analysis, […]
Exploring the Advantages and Features of Veterinary Operating Tables
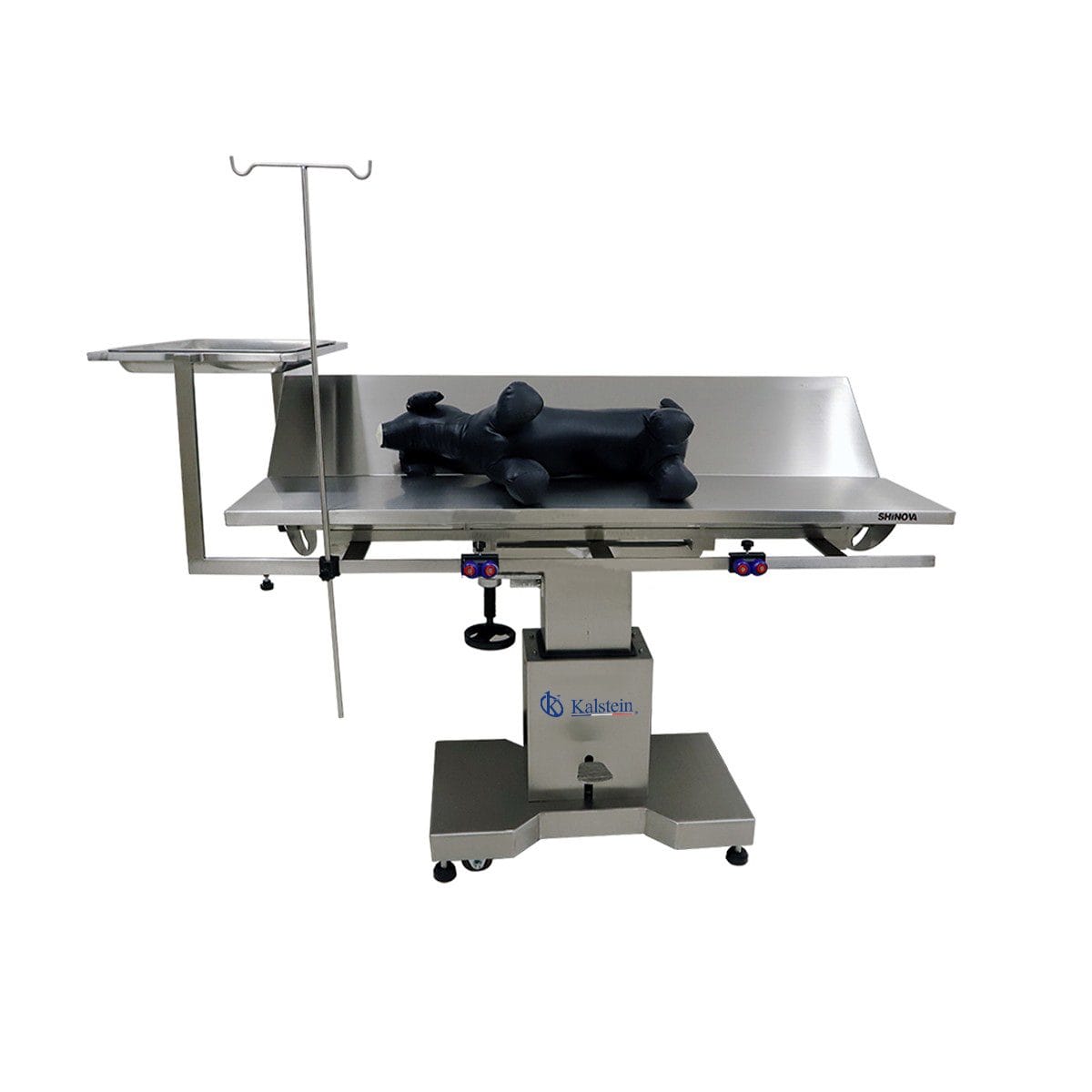
Veterinary Operating Tables, Brand Kalstein When it comes to choosing the right equipment for animal surgeries, the quality and reliability of veterinary operating tables are paramount. As someone deeply involved in the veterinary field, I’ve had my fair share of experiences with different brands and models of operating tables. My journey with specifically Kalstein’s Veterinary […]
Exploring the Excellence of Patient Monitors: A Deep Dive into Kalstein’s Outstanding Offerings
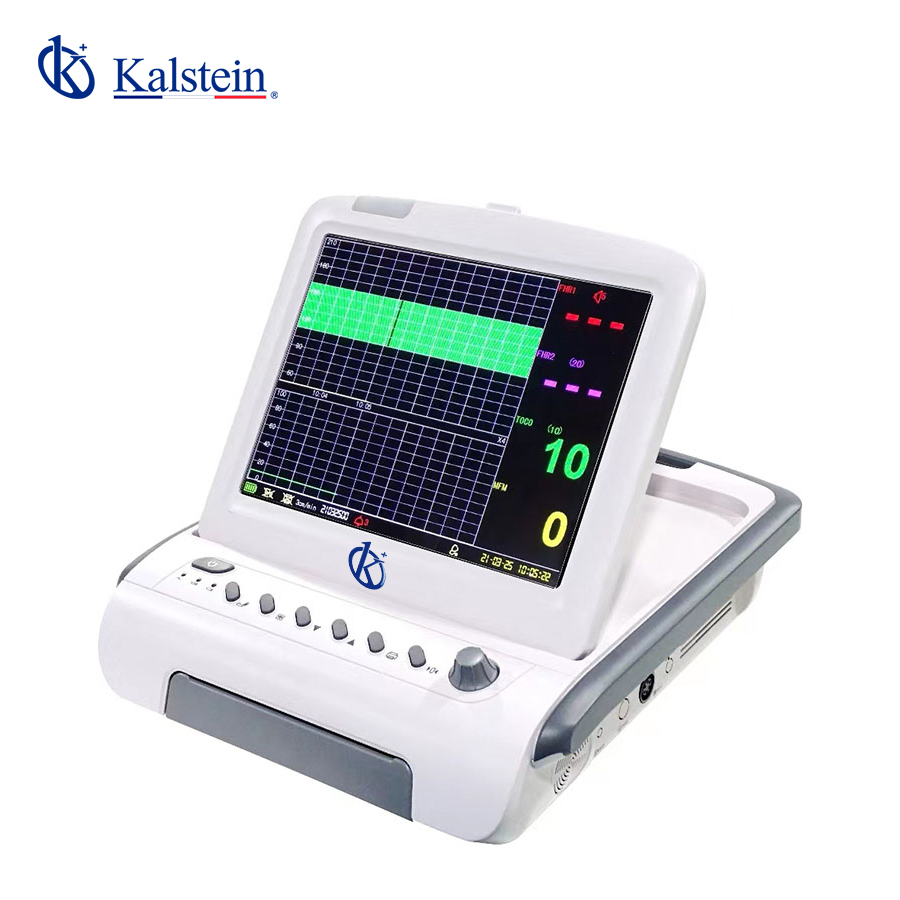
Patient Monitor: A Closer Look at the Kalstein Brand As someone who has had the opportunity to engage with various Patient Monitors in the medical field, I can’t help but appreciate the unique offerings presented by the Kalstein brand. Their commitment to quality and innovation is evident in every piece of equipment they produce. The […]
The Ultimate Guide to Vertical Laminar Flow Clean Bench: Ensuring Clean Environments with Kalstein
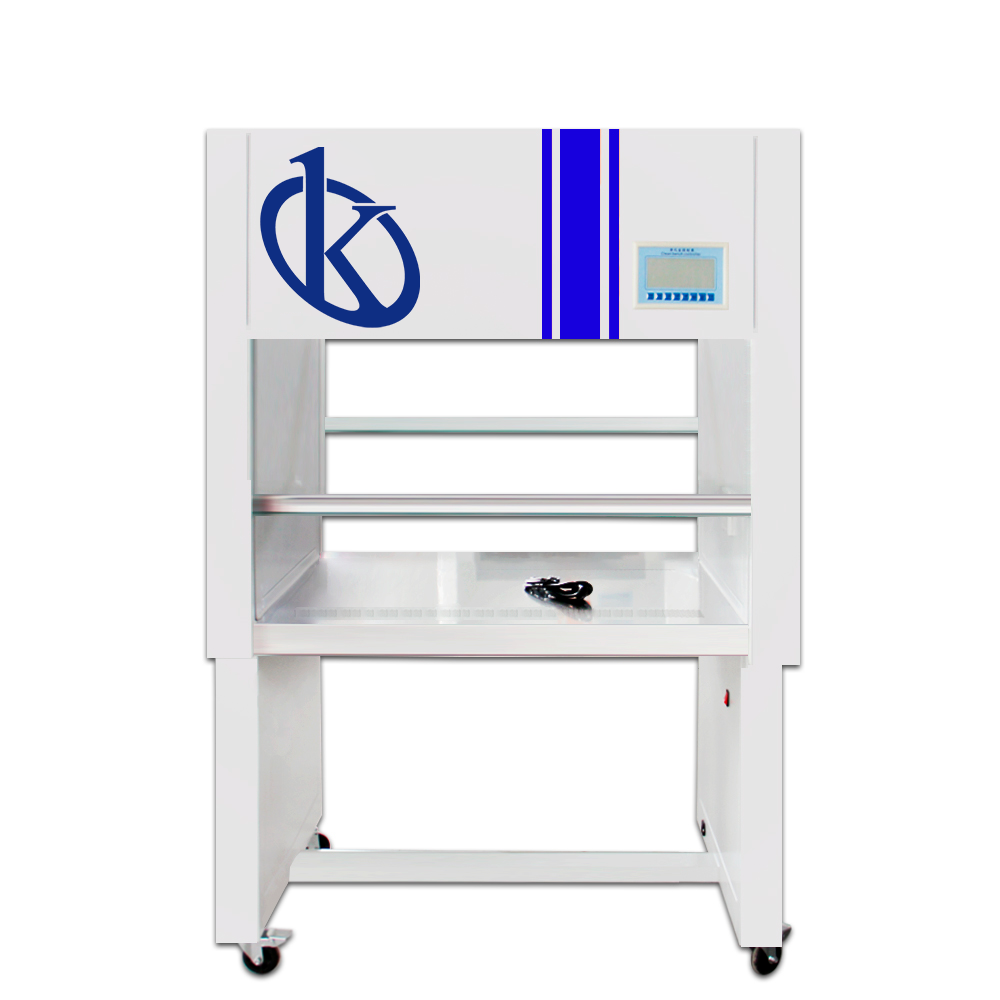

Kalstein’s Vertical Laminar Flow Clean Bench Kalstein is renowned for its state-of-the-art laboratory equipment, and the Vertical Laminar Flow Clean Bench is one of its flagship products. This equipment is specifically designed to maintain a clean and contaminant-free environment, which is essential for various laboratory applications, including microbiology, electronics assembly, and pharmaceuticals. Leveraging advanced technology, […]
Precision Balance Comparison: Kalstein vs. Adam Equipment
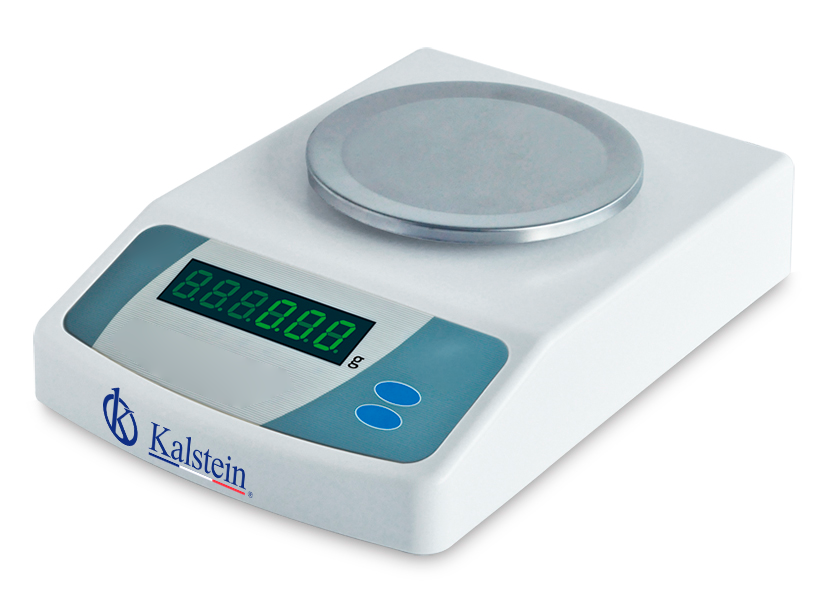
When it comes to laboratory balances, precision and reliability are paramount. Kalstein’s Precision Balance YR05588 // YR05593 and Adam Equipment’s Pinpoint Plus Balance offer state-of-the-art technology designed to meet the exacting demands of the scientific community. Both products cater to professionals who require accurate measurements, but they do come with unique features that set them […]
