Laboratory Centrifuges
The centrifuge is an essential laboratory equipment that generates rotation movements in order to separate the components that constitute a solution. This equipment applies a sustained centrifugal force (that is, a force produced by rotation) to push the matter out of the center of rotation.
Centrifugation is a technique governed by Stokes law, which proposes that particles settle more easily as long as they are larger in diameter and specific weight, and when their viscosity is lower. Centrifugation is used to isolate or concentrate suspended particles in a liquid taking advantage of the different speed of displacement according to its shape, size or weight when subjected to a centrifugal force. Centrifugal force is the force exerted on a body when it rotates around an axis.

Types of Centrifuges a Laboratory may need

Non-refrigerated Centrifuges
At Kalstein we are specialists in the manufacture of laboratory equipment, and our clinical centrifuges usually have a wide variety of advantages, such as:
- Ease of operation and the best technology.
- Accident safety device.
- Guarantee of separation of the components of a mixture.
- They have legs covered with non-slip material to fix on tables or inns.
- Ease of cleaning, maintenance and safety.
- They have a rotor that avoids loud noises and vibrations.
- Models that provide economy, efficiency and durability.
Refrigerated centrifuges
It is a equipment used in the processes of the separation of the sedimentation of the liquid and solid components of a sample, this apparatus generates rotation movements and through the centrifugal force accelerates the decantation or sedimentation of the components of the sample, according to their density, there are different types of centrifuges, which pursue the same objectives.
In laboratories centrifuges produce a high speed rotation, separating layers of the different materials that make up the sample and that generates the densest elements of the sample to be deposited in the bottom of the container and the lightest ones to be kept in the top of it; the relative force of centrifugation is measured in multiples of gravity, and by its physical size cannot be represented in units.

In Kalstein you can find the ideal Centrifuges for your Laboratory
For each research or analysis there is a special type of centrifuge, and the type of centrifuge is determined by the value of the relative centrifugal force (F.C.R.), this is the force needed for particles to be separated. Depending on the speed range, there are several types of centrifuges.

High-speed refrigerated centrifuge YR0113
In this case, we present two models: YR0113 and YR0112. Both models are centrifuges used to collect microorganisms and cell samples...

High-speed refrigerated microcentrifuge YR111-5
This multipurpose centrifuge has advanced and intelligent technology. Control by microcomputer, large LCD touch screen...

High-speed Centrifuge Table YR0125
The main operating principle of high-speed centrifuge: high-speed centrifuge is the powerful centrifugal force...

High-speed refrigerated centrifuge YR0111-3
The centrifugal tubes for high-speed centrifuges are typically manufactured from plastic and polypropylene...
Our best-selling Lab Centrifuge
Refrigerated high-speed centrifuge table YR0125
The main operating principle of the high-speed centrifuge: high-speed centrifuge is the powerful centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the frozen centrifuge rotor of the high-speed centrifuge to accelerate the sedimentation rate of the particles in the liquid and separate the sedimentation coefficient and flotation density from the sample.
Centrifuge is a type of machine that performs solid-liquid, liquid-liquid or solid-liquid phase separation under the action of centrifugal force. The rotor is the main component of centrifuge. It is mostly made of titanium alloy or aluminum alloy. It is installed at high speed. The separation is achieved by centrifugal force on the vertical or horizontal axis, and can be used for centrifugal separation separation separation, centrifugal filtration and centrifugal sedimentation. The separation factor is the main indicator of centrifugal separation performance. It is the relationship between centrifugal force and material gravity, which is equal to the ratio of centrifugal acceleration to gravity acceleration.
| Model | YR0125 |
| Maximum speed | 20,000r/min |
| RCF Max | 27,800 xg |
| Speed Accuracy | ±50r/min |
| variety of gold | -20°C ~ +40°C |
| Heat Exposure | ±1.5°C |

Analysis of the best Centrifuges for your Laboratory

Centrifugation: RPM vs. force g
The relative centrifugal force or g force (RCF) is the amount of acceleration to be applied to the sample in the centrifugation process. Depends on revolutions...

What is a microcentrifuge?
A microcentrifuge is a special type of centrifuge that serves the function of centrifuging samples that are in small capillary tubes, in order to separate the components...

Centrifuge: Types of rotor
The two main types of rotors that are used in laboratory centrifuges are horizontal (also called tilting hub) and fixed-angle (or angled head) rotors.
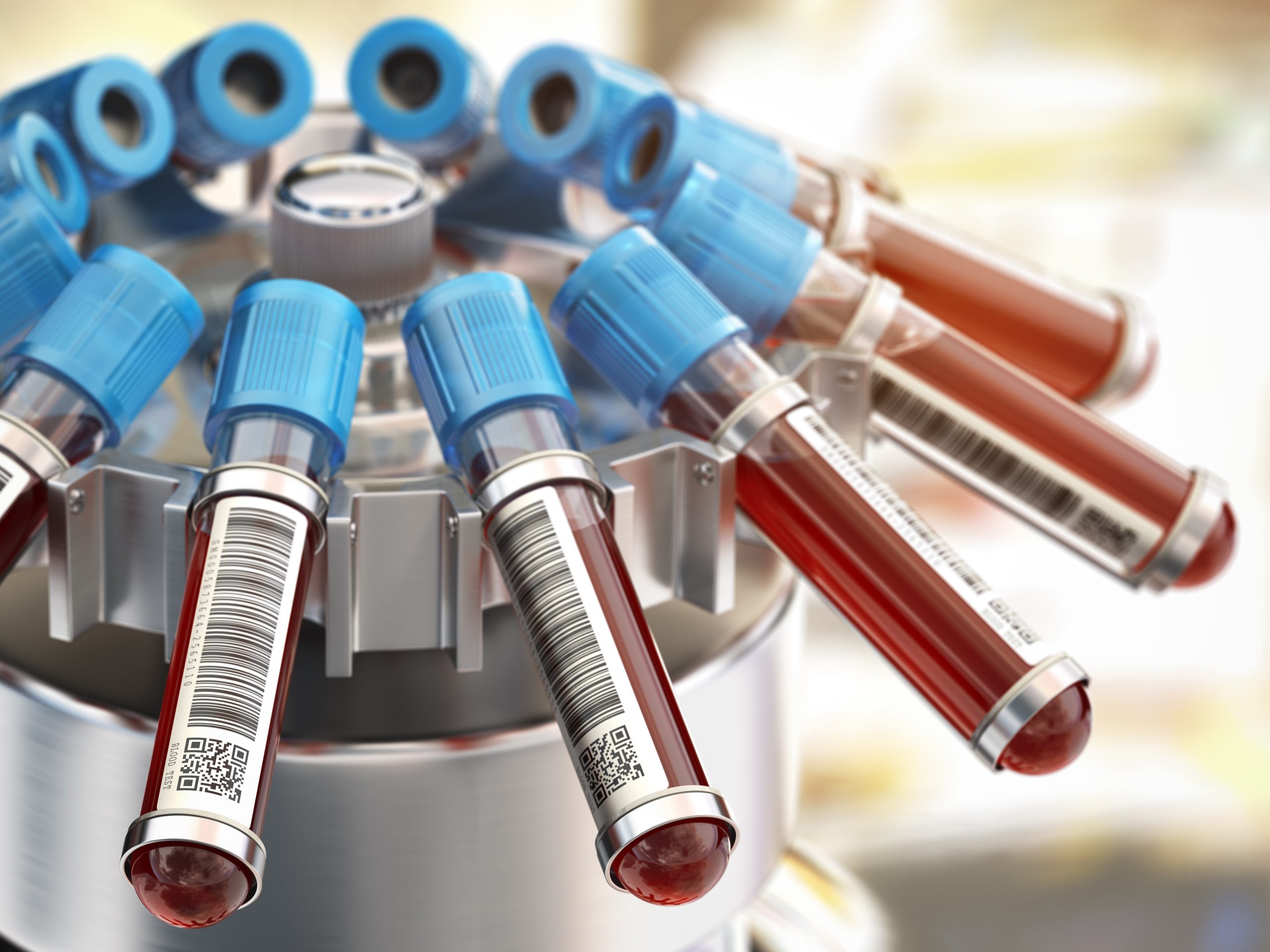
What is a clinical centrifuge?
A clinical centrifuge is a laboratory instrument that separates cellular components, blood plasma and serum, cellular elements from urine samples and other...
Catalog of Centrifugas models on offer
-

High-speed table centrifuge YR137-2
Select options -
Centrifuge PRP YR469
-

Speed table centrifuge YR134
Select options -

Low speed table centrifuge YR0140-1
Select options -
Speed table centrifuge YR0140
Select options -

Low speed centrifuge YR124-1
Select options -

Cytocentrifuge YR53-CYTO
-

Mini centrifuge YR144.
Guides for you to become an expert in Centrifuges
Refrigerated Centrifuges function
To use a refrigerated centrifuge it is necessary to follow a series of steps that allow its safe operation. While teams of this kind in general terms...
What is a hematocrit Centrifuge?
The hematocrit test is a type of blood test. The blood consists of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Blood cells and platelets are suspended...
What is a high-speed Centrifuge?
High-speed centrifugation is an irreplaceable tool for the isolation and characterization of multiple biological structures: from biomolecules, like acids...
How to act in case of the rupture of tubes inside a Centrifuge?
In order to use a centrifuge it is necessary to follow a series of steps that allow its safe operation. While equipment of this type generally operates in the same way, it is advisable to consult the manual...
Centrifuges videos in operation
In this section you will find our Centrifuge in operation, packed, receiving service, etc.
Process of using Centrifuges
These medical equipment thanks to its function are not only necessary and used in laboratories, but also in clinics, public health centers, among others where the separation of solutes from their solvents is required, at the time of cleaning and maintenance we must recognize the parts and accessories of the centrifuges to establish a maintenance routine, according to the type of centrifuge, among the variety of these machines we have: low-speed serum or plasma separation centrifuges, centrifuges for microhematocrits and ultracentryfuges for protein separation.

Frequently asked questions about Centrifuges from our customers
How to know the prices of Centrifuges?
To know the price of centrifuges we invite you to send us an email with your request through the contact form.
What are the delivery times for Centrifuges?
The delivery time of your Kalstein product will depend on the following:
- If the equipment of your interest is in stock or if on the contrary it should be manufactured.
- The type of freight you have chosen may be; air or sea.
- Equipment in stock:
– Delivery Time (Aereo): 15-30 days.
– Delivery Time (Maritimo): 45-60 days.
- Equipment not in stock:
– Delivery Time (Aereo): 30-60 days.
– Delivery Time (Maritimo): 60-90 days.
How to make a purchase of Centrifuges?
You can make your purchase through:
- By email: [email protected]
- By phone: +33 (0) 1 78 95 87 02
- Electronic commerce: Through Kalstein's official website in his country.
How does the warranty work?
Can I request a quote online?
Of course, you can request a quote for the Kalstein team of interest, directly from our official website. Once you have identified the model of your choice, click HERE
