Pathological anatomy
Pathological anatomy or anatomous-pathology is the human and veterinary medical discipline that allows the recognition of macroscopic and microscopic abnormalities of biological tissues and pathological cells taken from living or deceased beings. The pathological anatomy allows the recognition of cellular and tissue anomalies, called lesions, to make a diagnosis, they made a prognosis and understand the causes and mechanisms of anomalies.
Pathologists use several appliances in addition to the microscope: specialized specialized baths for histology, paraffin distributors, refrigerated plates, tissue processing machines, paraffin inclusion stations.

Types of Pathology a Laboratory May Need

Cooling plate
This equipment is indispensable in any laboratory of pathological anatomy, mainly in the area of histology, since the cooling process is essential to make sections of paraffin blocks of good quality, besides that it is impossible to make efficient cuts without the cooling plate, the use of this equipment ensures that the cutting is much easier and effectively improves the paraffin blocks, saving considerable time.
The cooling plate model that we offer you in KALSTEIN, is a cryoplate adopted with a new inverter compressor, which makes the paraffin blocks of the fabric cool quickly. This model has a Teflon coating, which ensures easy cleaning, so you don't have to worry about it.
Automatic Slide Stainer
La automatización de la tinción de los portaobjetos, es una herramienta fundamental en los laboratorios que necesiten aumentar en rendimientos para sus estudios. Este equipo, efectúa programaciones de tinción estandarizadas, y permite al personal de laboratorio, ahorrar tiempo.
Asimismo, los laboratorios de microbiología general e histología, que buscan reducir la carga de trabajo de tinción de muestras, se beneficiarán enormemente de su uso. Hasta más de 20 portaobjetos de microscopio, se cargan en el cesto del equipo.

In Kalstein you can find the ideal Pathology Equipment for your laboratory

Automated microtome YR415-1
The feeding system uses an intelligent control mechanism; enabling quick switching between manual or automated...

Cryostat Microtome YR426-1
The YR426-1 Cryostat Microtome is belong to one class medical equipment. It is a device for rapid pathological...

Flotation work station YR452
High-quality Tissue flotation station YR452 with keyboard control, microcomputer automatic memory, LED ...

Slide Dryer (Oven) YR453
High-quality hot plate with keyboard control, microcomputer automatic memory and digital tube display. This model...
Our best-selling Pathology team
- Pure-green digital screen for real-time monitoring of heating temperature, direct and clear, easy to operate; all parameters including preset temperatures, working temperatures, and wording status are real-time displayed
- Temperature is automatically program-controlled by single-chip microprocessors
- This device features multiple functions and its easy setting operation can meet the needs of different users
- DC low-voltage illuminating system and removable transparent heating dish: easy operation and convenient observation...
| Model | YR457 |
| Temperature range of water bath | RT – 70℃; automatically maintained |
| Temperature range of slide dryer | RT – 100℃; automatically maintained |
| Automatic memory and restoration functions | After startup, all preset temperature data are automatically stored in the system. |
| Temperature Control Precision | ±2℃ |
| Dimensions of water bath dish | 210×170×60mm(W×D×H) |
| Dimensions of drying station(50pcs slides) | 250×108mm(W×D×H) |
| Working Voltage | AC 220V±10% 50Hz (standard model) |
| Power | 400W |
| Dimensions | 460×310×135 mm (W×D×H) |
| Net weight | 6kg |

Analysis of the best Pathology equipment for your laboratory

Tissue water bath
Water baths are a very common element in any type of microbiological laboratory. This type of equipment is a...

What is a cryostat?
The cryostat is a piece of equipment used in the processing of samples for histological or histopathological ...
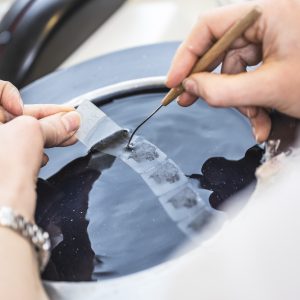
What is a microtome for?
Microtomy is the discipline that deals with obtaining fine serial sections from tissues included in paraffin blocks...

What is pathological anatomy?
Pathological anatomy is the science that studies the pathophysiological and morphological alterations ...
Catalog of Pathological Anatomy models on offer
Guides to Becoming an Expert in Pathological Anatomy
What tests are performed in a pathology laboratory?
This area of medicine studies the morphological basis of the disease, that is, it is based on direct observation...
The microtome and bone cutting in pathology
The microtome is a mechanical instrument used to cut biological samples into very thin segments for microscopic...
Tissue processing for histological pathology studies
Tissue processing is a very important part of any histology laboratory, and begins with obtaining the tissue under..
What does a pathologist do? What is a pathology laboratory?
A pathologist is a doctor who specializes in pathological anatomy, a science that studies the pathophysiological and morphological alterations of the disease, that is, it studies the disease from its organic, tissue, cellular, subcellular...
Video of Pathological Anatomy Equipment in Operation
In this section you can find, our pathology teams in operation, packaged, receiving service, etc.
Microtome running
A laboratory of pathological anatomy, is a specialized laboratory, where biopsy and cytology samples are processed by highly qualified personnel, for subsequent microscopic examination, interpretation and diagnosis by a pathologist doctor. This science not only studies the evolution and causes of a disease, but also makes a forecast of the effects that different diseases can have on humans. For this, tumor cells and body tissues are analyzed.
Thus, the pathologist or anatomopathologist identifies the causes and consequences of diseases that affect specific parts of the body, through microscopic analysis of tissue or cell samples, previously prepared with special dyes that help to identify structural alterations, in cells and tissues, as well as protein or genetic abnormalities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Anatomy Pathology Equipment
How to know the prices of the pathological anatomy equipment?
To know the price of the equipment of Pathological Anatomy we invite you to send us an email with your request through the contact form.
What are the delivery times of the pathological anatomy teams?
- If the equipment of your interest is in stock or if it must be manufactured.
- The type of freight you have chosen, this may be; air or sea.
How to make a purchase of Pathology equipment?
- By email: [email protected]
- By telephone: +33 (0) 1 78 95 87 02
- E-commerce: Via Kalstein's official website in your country.
How does the warranty work?
All Kalstein equipment has a 1-year warranty against manufacturing defects. The warranty does not cover damage caused by poor installation or operation by the user, transport defects or by uses other than those specified by the manufacturer. Warranty excludes electrical or consumable parts. For more information visit our “Terms and Conditions ” by clicking HERE
At Kalstein, we provide our customers with induction and technical support through new online methods. You can visit our induction videos, technical assistance and guidance provided by a Kalstein team through our channel Youtube (Kalstein English). HERE
Can I request a quote online?
Of course, you can request a quote for the Kalstein team of your interest, directly from our official website. Once you have identified your preferred model, click HERE








